Laboratory for Raw Materials and Recycling
One of our specialties is mechanical process engineering, which is primarily used in environmental technology, especially in recycling plants. However, our clients also include producers of primary raw materials, such as gravel plants. Accordingly, our equipment is set up to be highly versatile.
Comminution
Various devices are available for the comminution of samples (plastics, metals, bulk materials, and similar). Depending on the material properties and desired outcome, different comminution methods and levels of comminution can be selected.
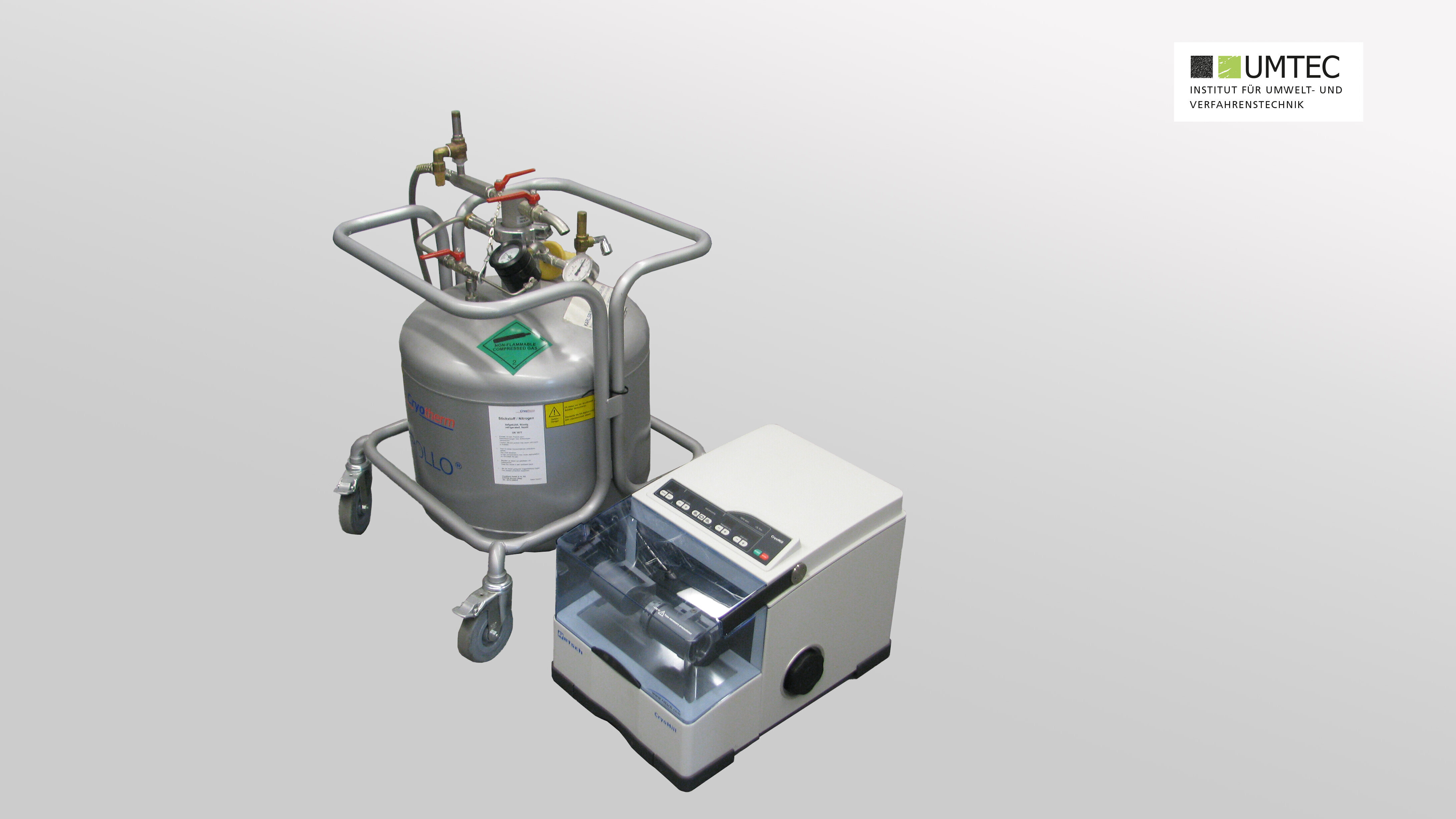
Cryomill (Retsch / Laboratory)
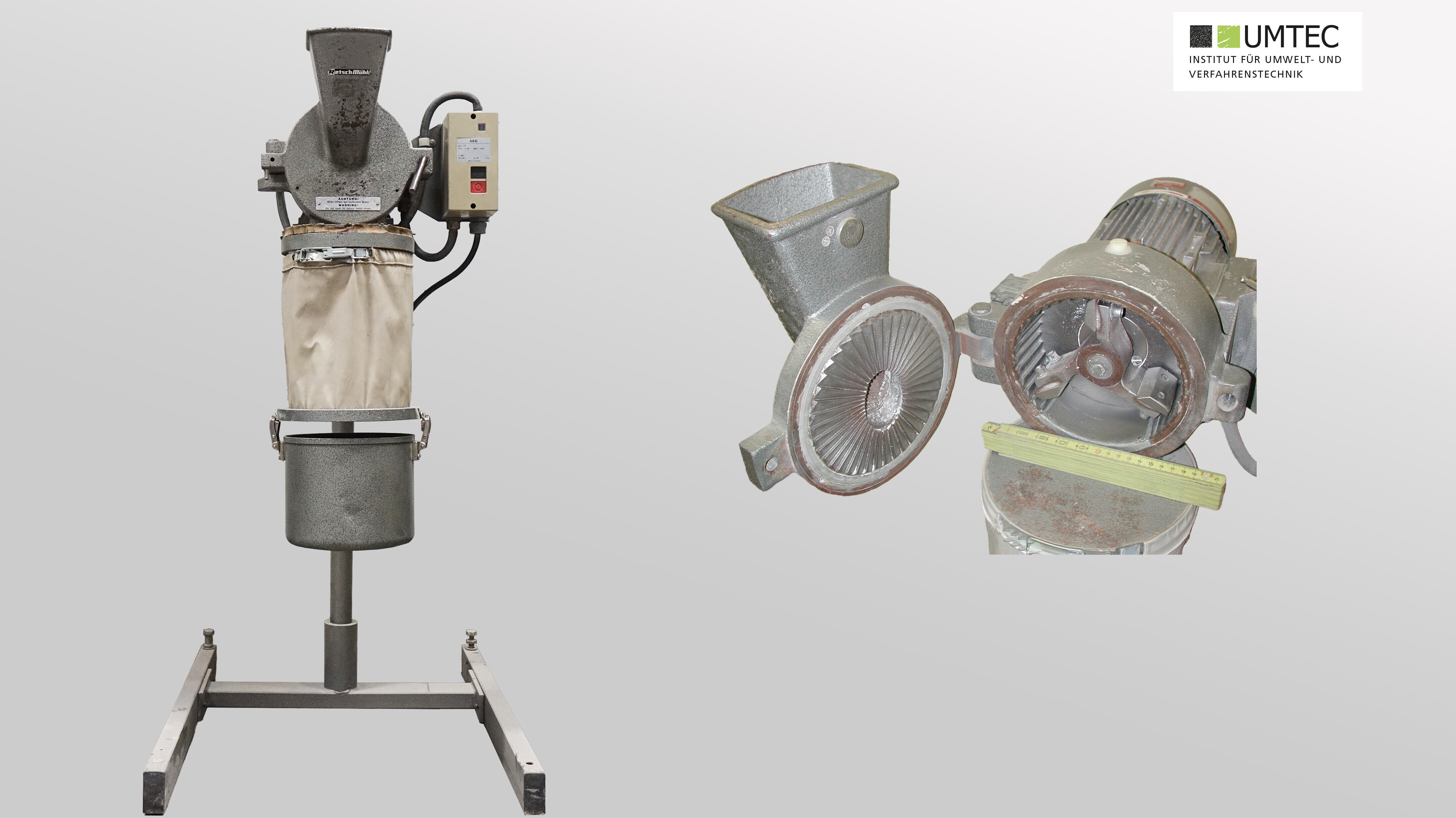
Jaw Crusher (Retsch BB400 XL)
Roll Crusher (Sieving Technology / Laboratory)
Cross Beater Mill (Retsch / Laboratory)
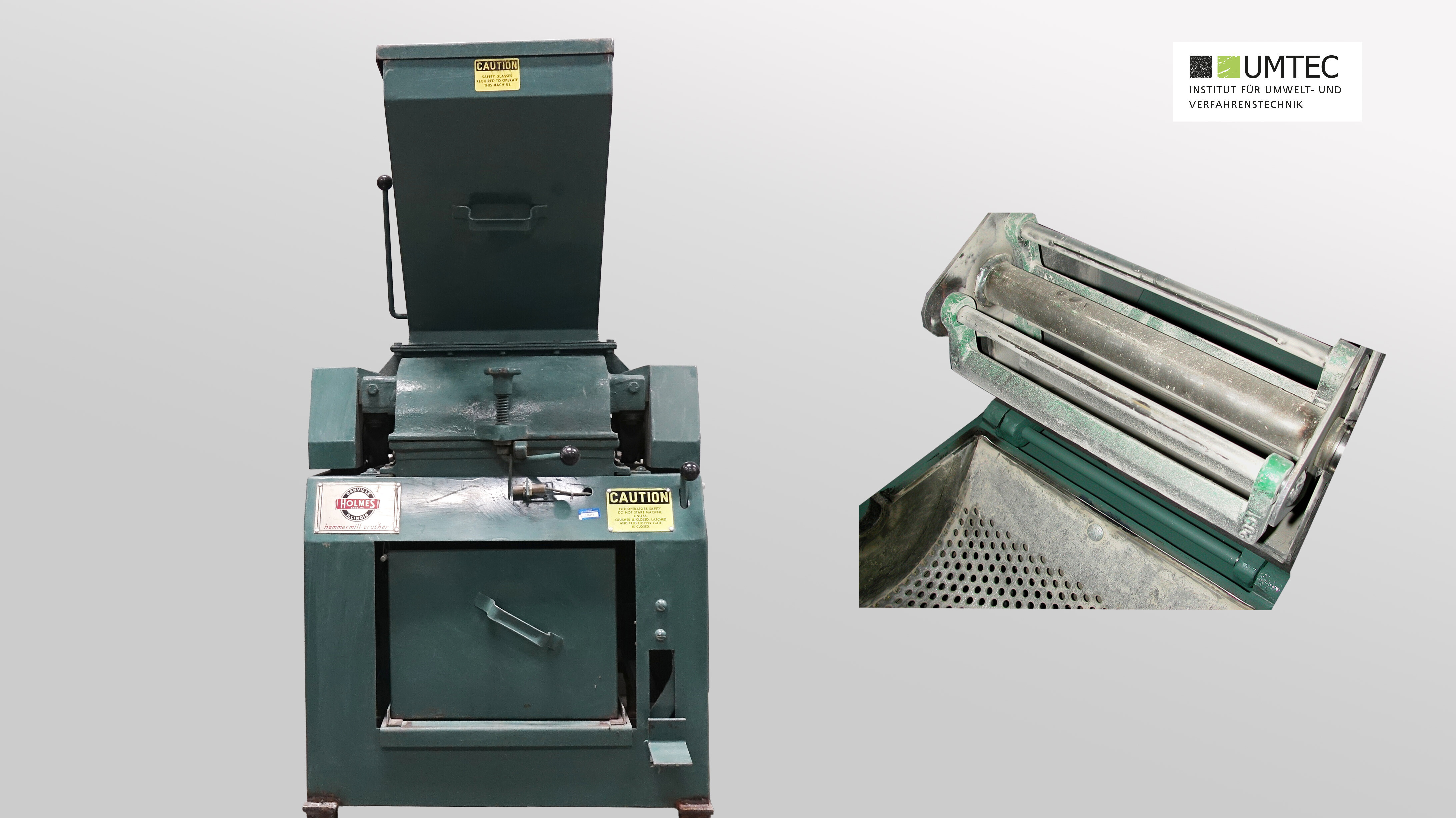
Hammer Mill 401XL (Holmes Bros. / Pilot Scale)
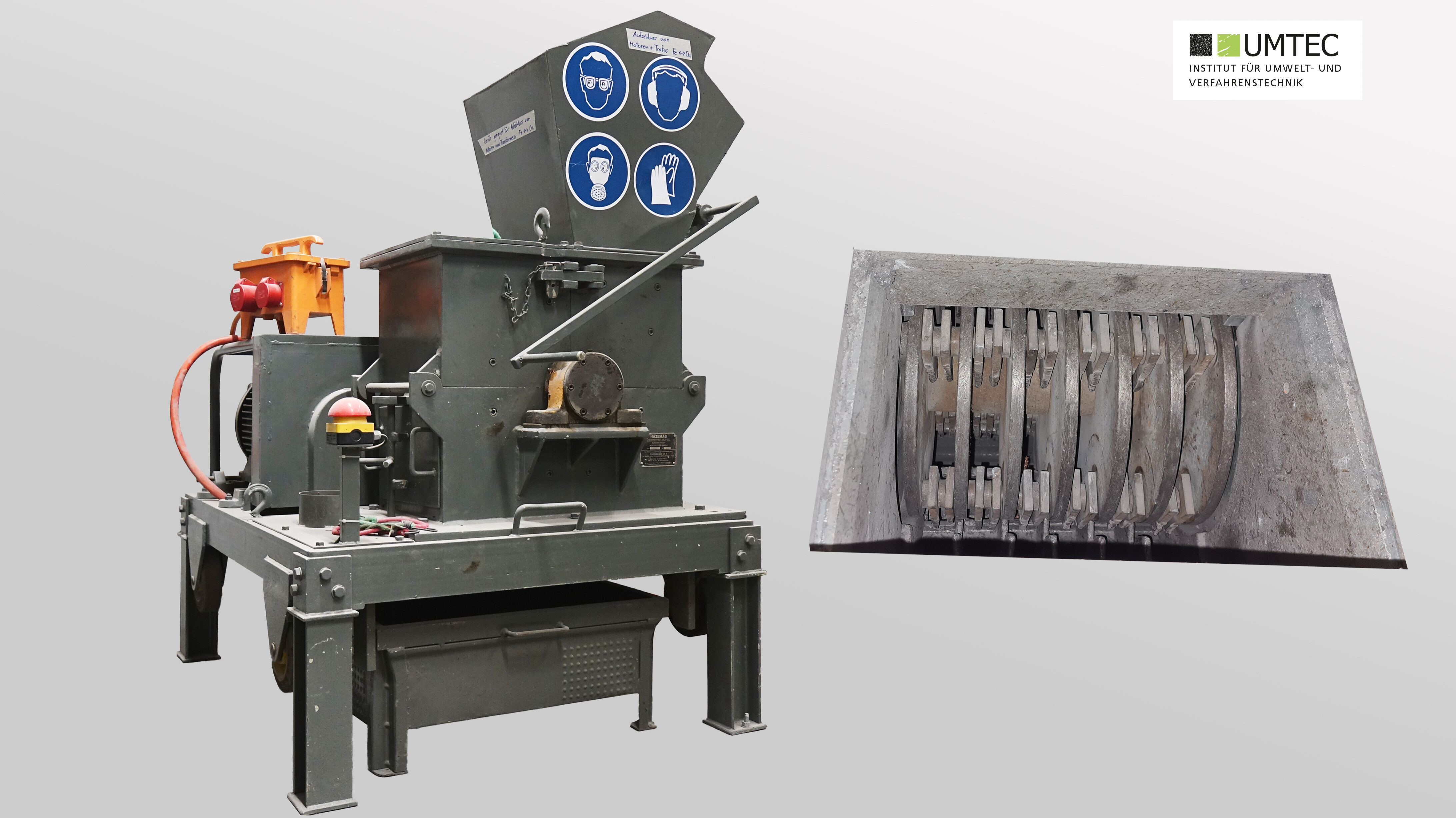
Hammer Mill Unirotor 490/380M (Hazemag / Pilot Scale)
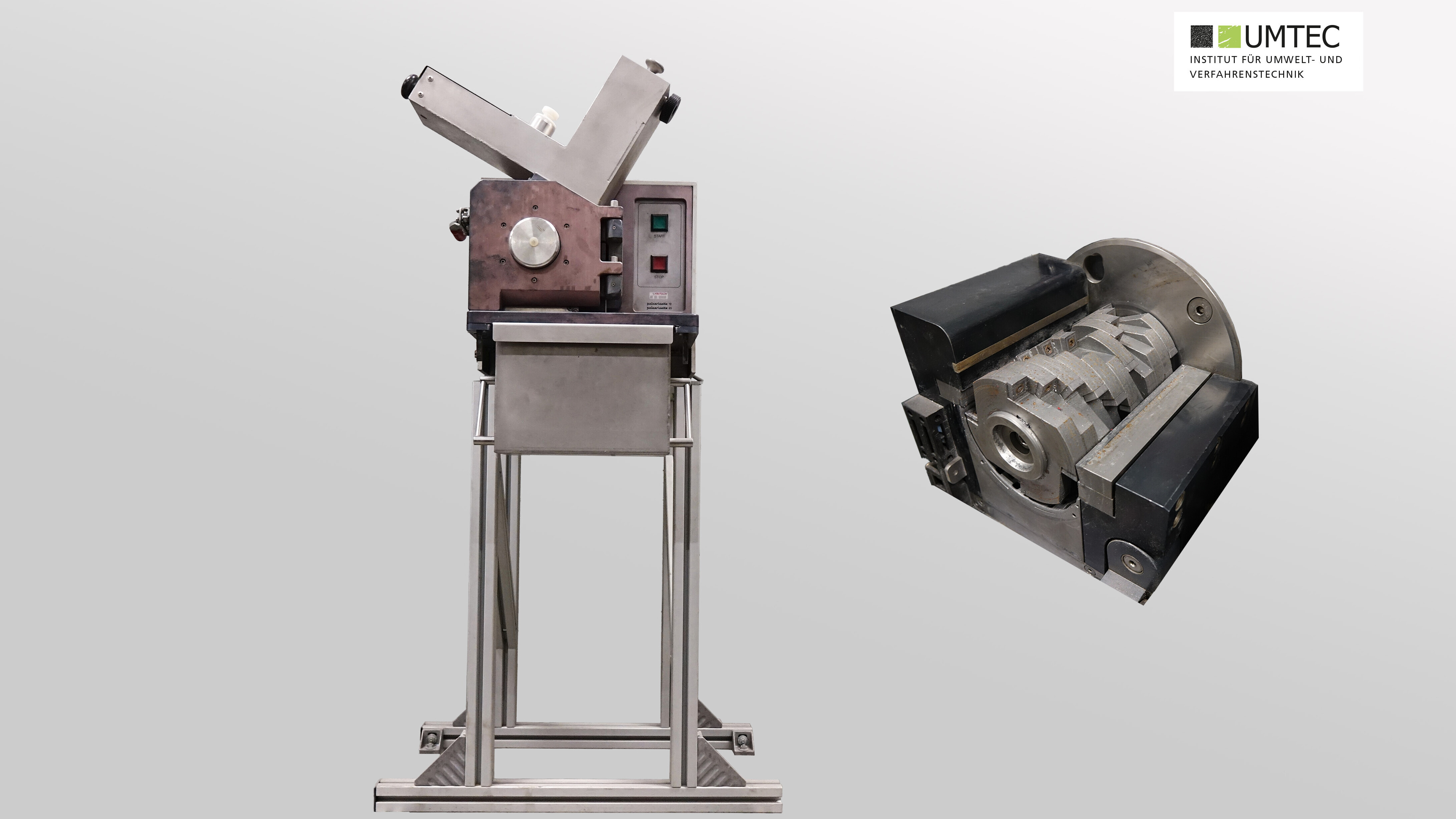
Cutting Mill (Fritsch Pulverisette 25 / Laboratory)
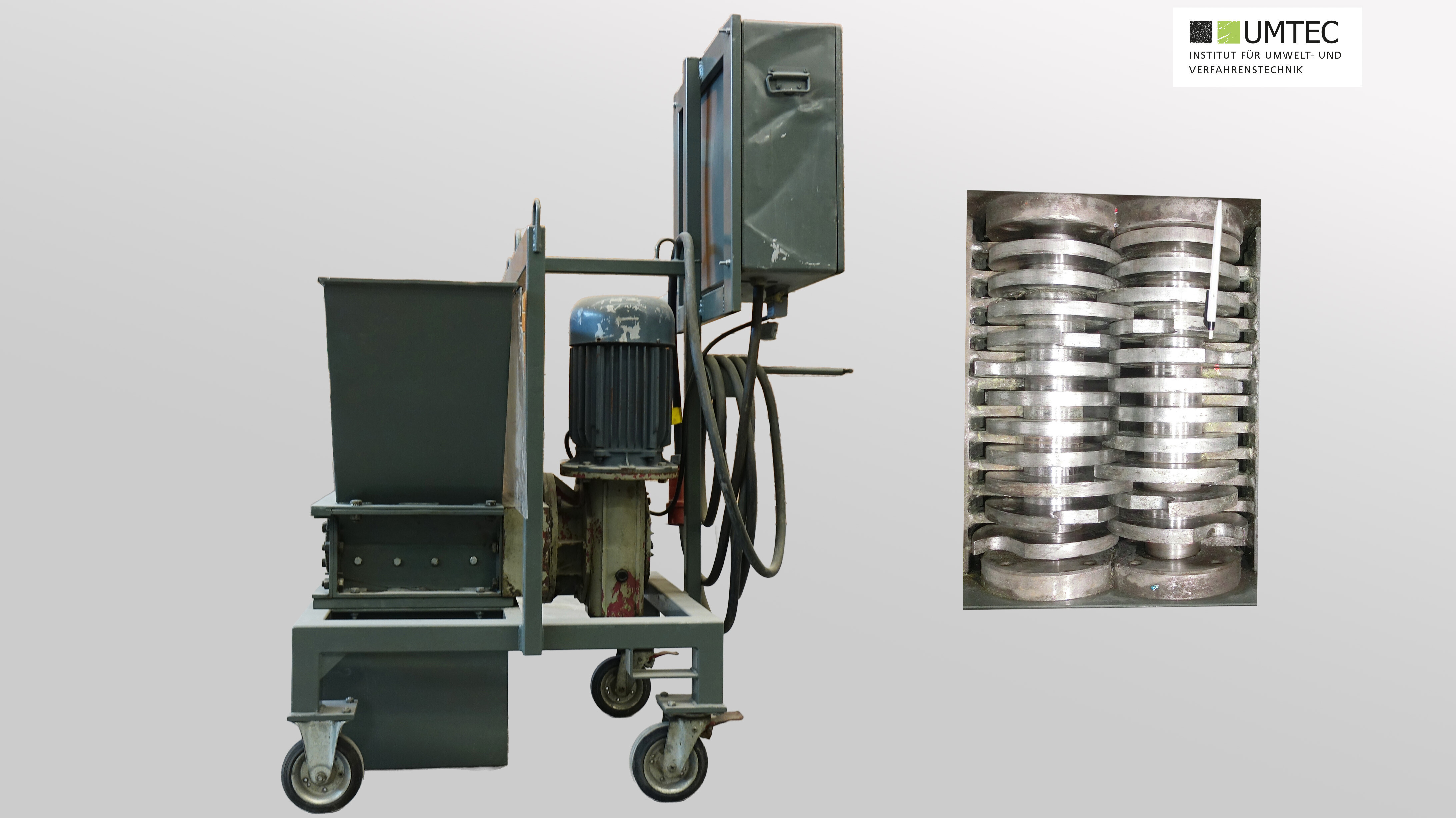
Rotor Shear (Trummer & Co / Pilot Scale)
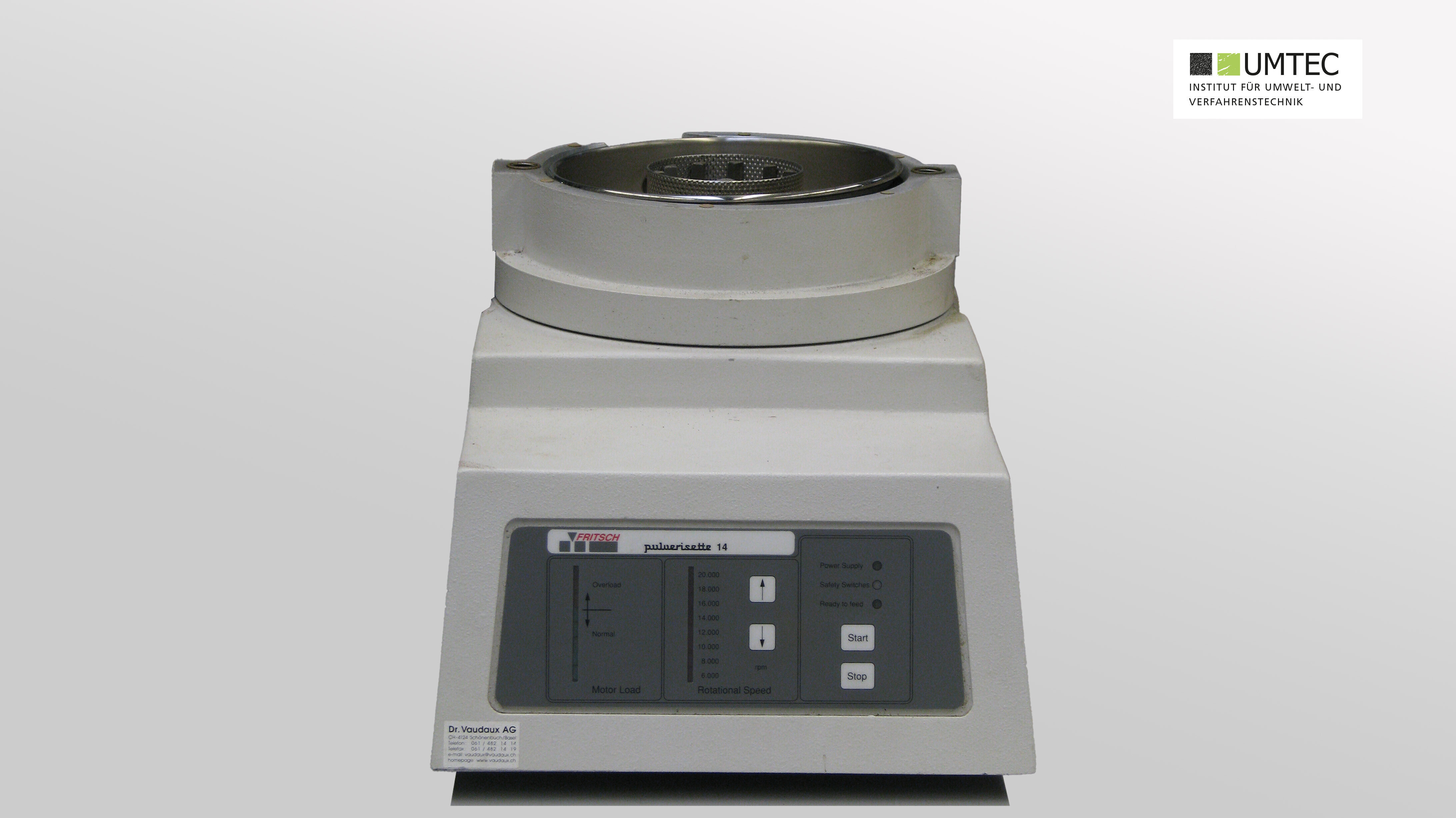
Rotor Impact Mill (Fritsch Pulverisette 14 / Laboratory)
SMASHER (In-house Development / Laboratory)
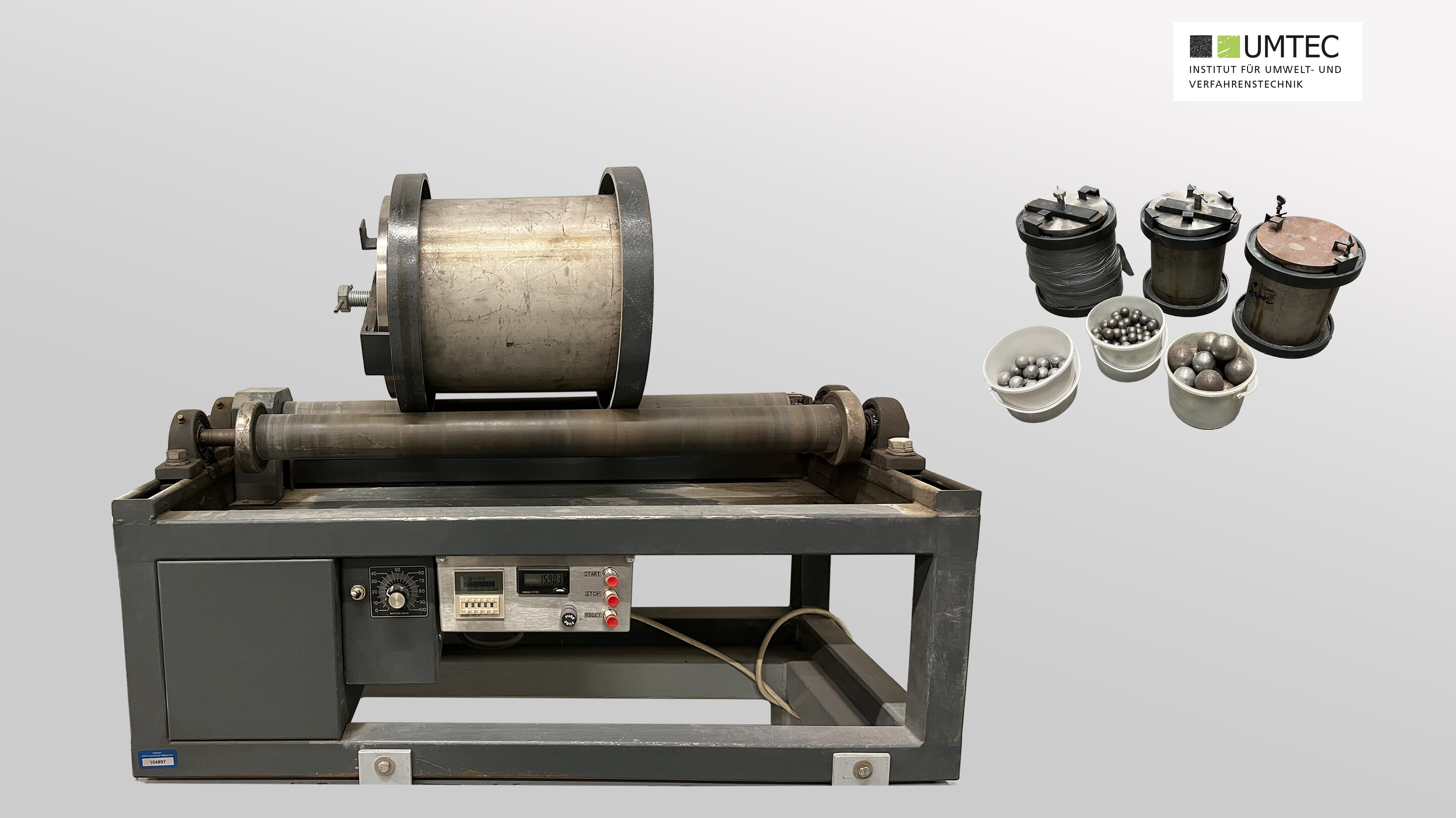
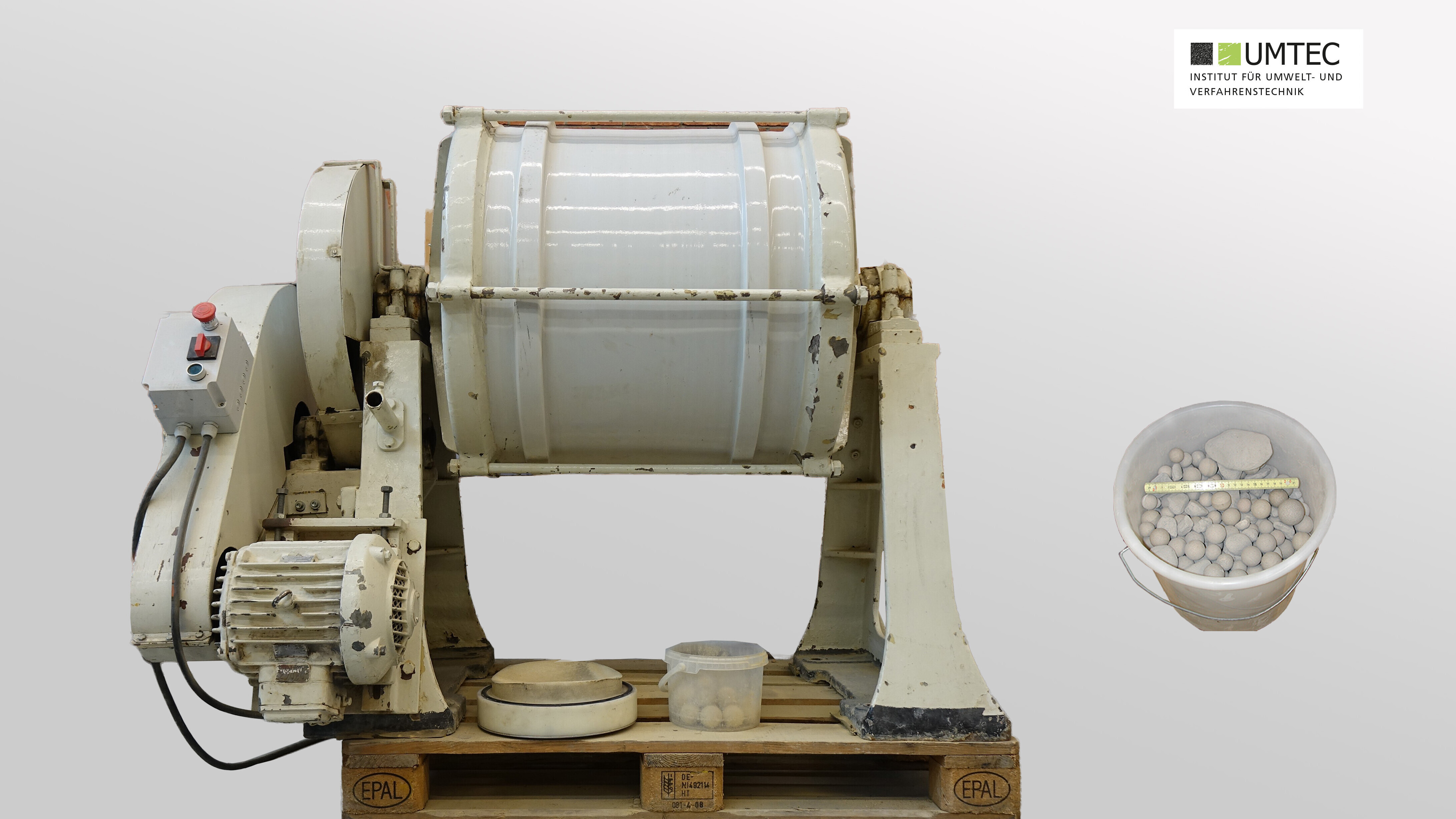
Roller Table with Ball Mill Container (Sepor / Laboratory)
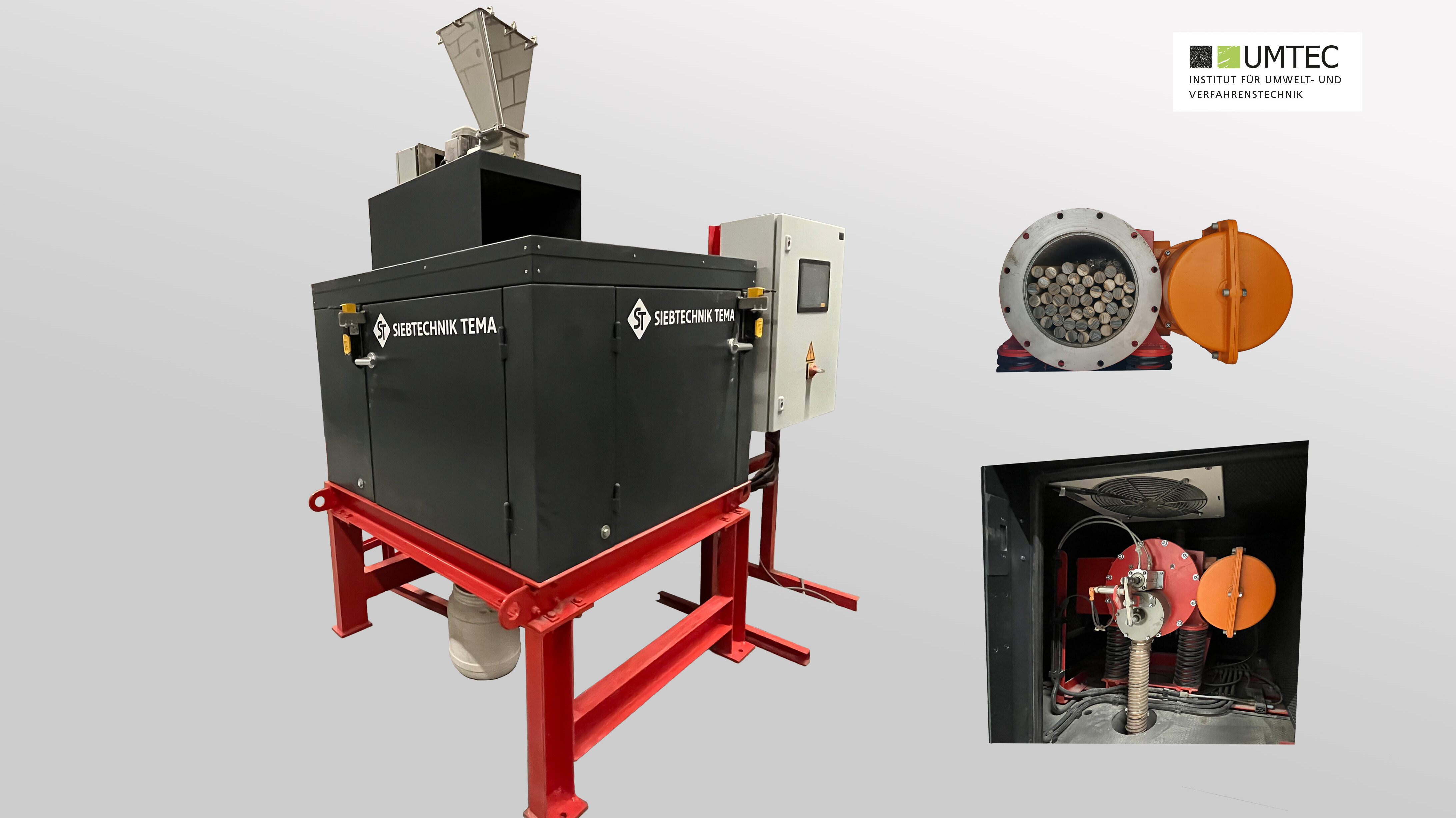
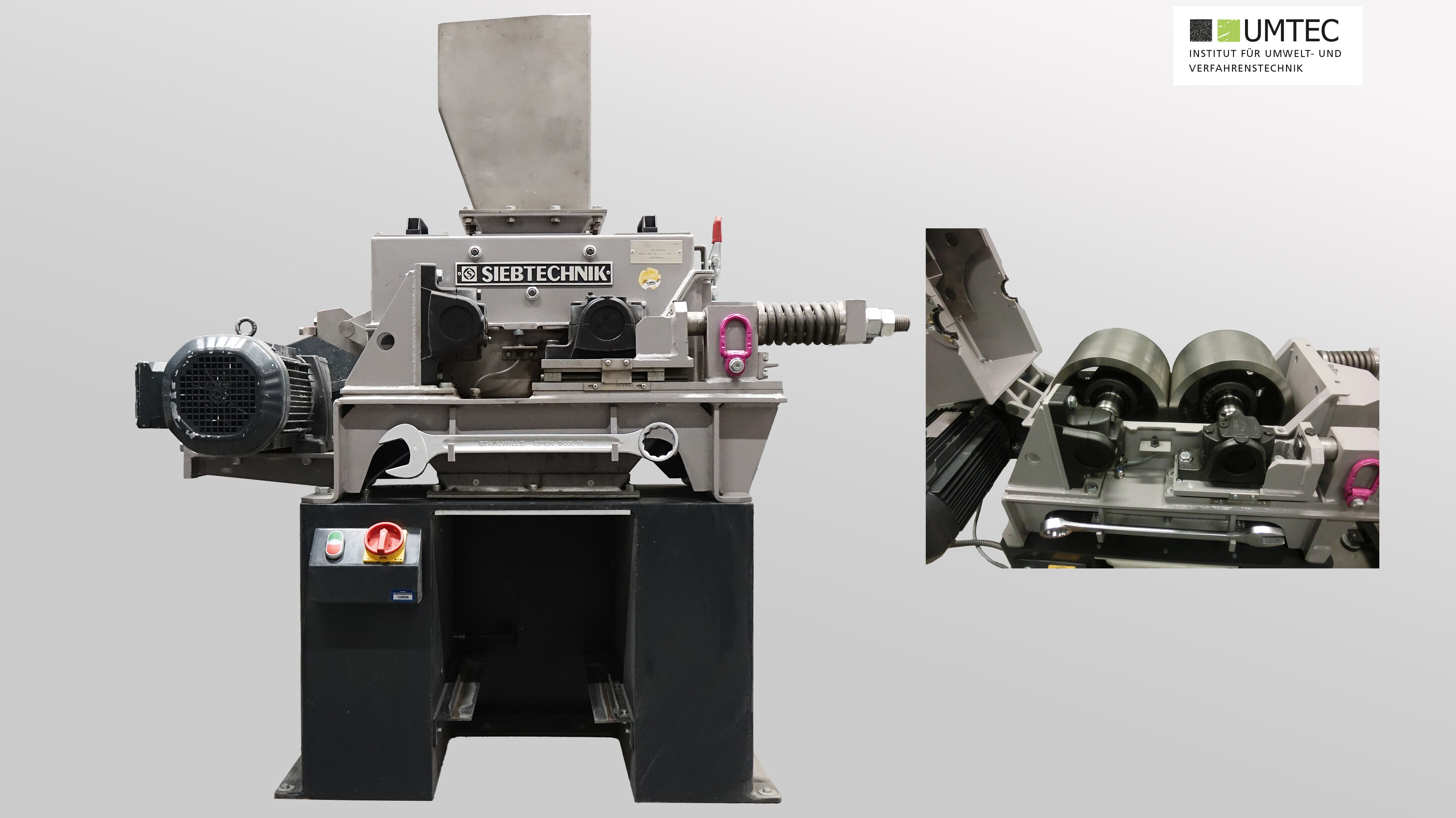
Tube Vibrating Mill (Siebtechnik ESM236-1bs / Pilot Scale)
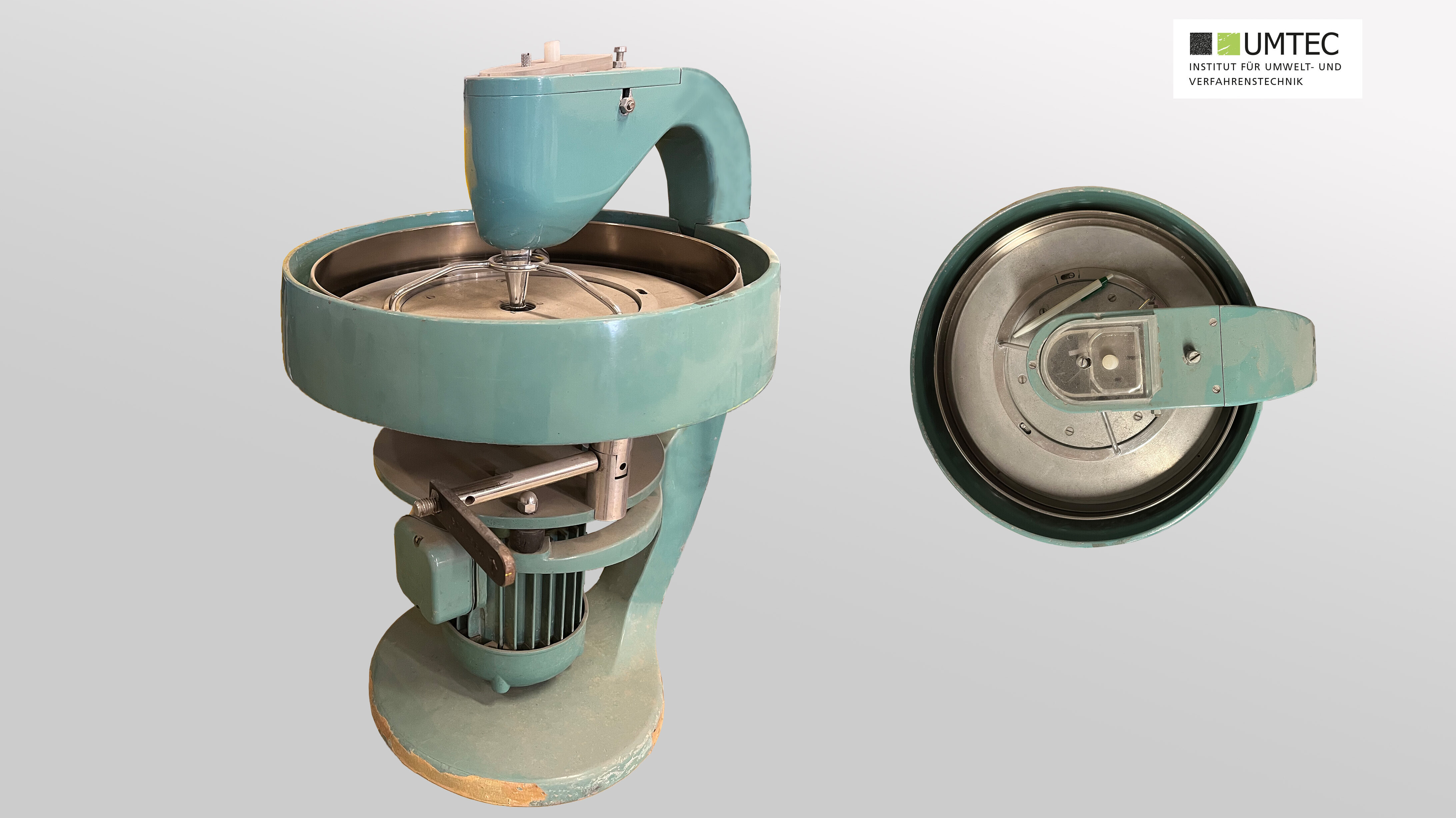
Disc Mill (Retsch RS300 / Pilot Scale)
- Fast, loss-free and reproducible ultra-fine grinding of medium-hard, hard, brittle and fibrous materials to analytical fineness
- The disc with the grinding set performs a three-dimensional oscillation. The grinding media in the bowl exert extreme pressure, impact and friction effects on the material to be ground due to the oscillating movements of the drive.
- Batch operation
- Nominal speed 912min-1
- 2000ml grinding bowl made of chrome steel
- Output grain size <20mm
Classification
Various devices are available for the separation of a granular bulk material into individual particle classes of different sizes (classification). Depending on the desired fraction size, different methods can be used. Additionally, depending on the apparatus, subordinate factors such as density can also be considered alongside particle size.
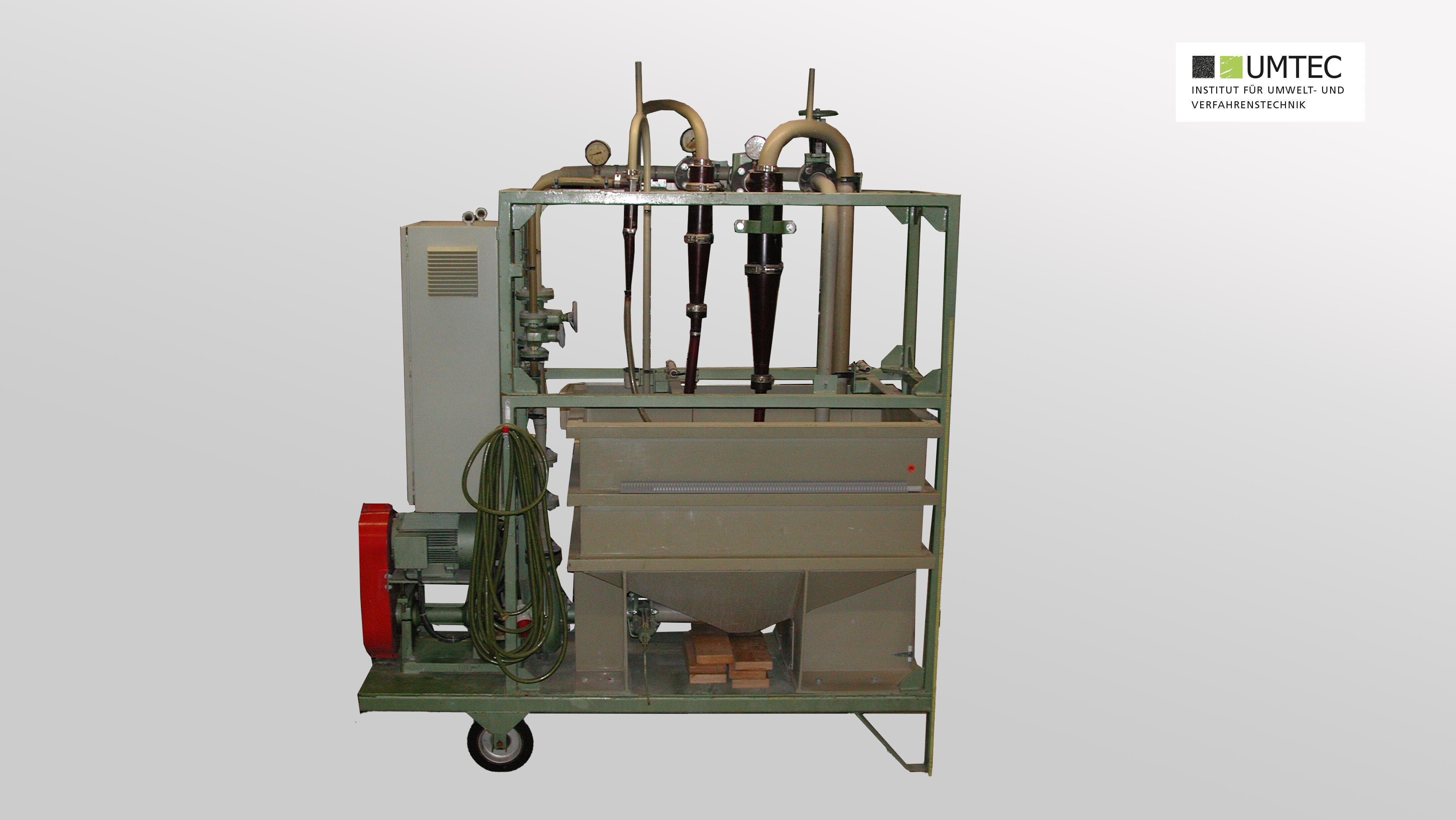
Cyclone Test Stand (Pilot Scale)
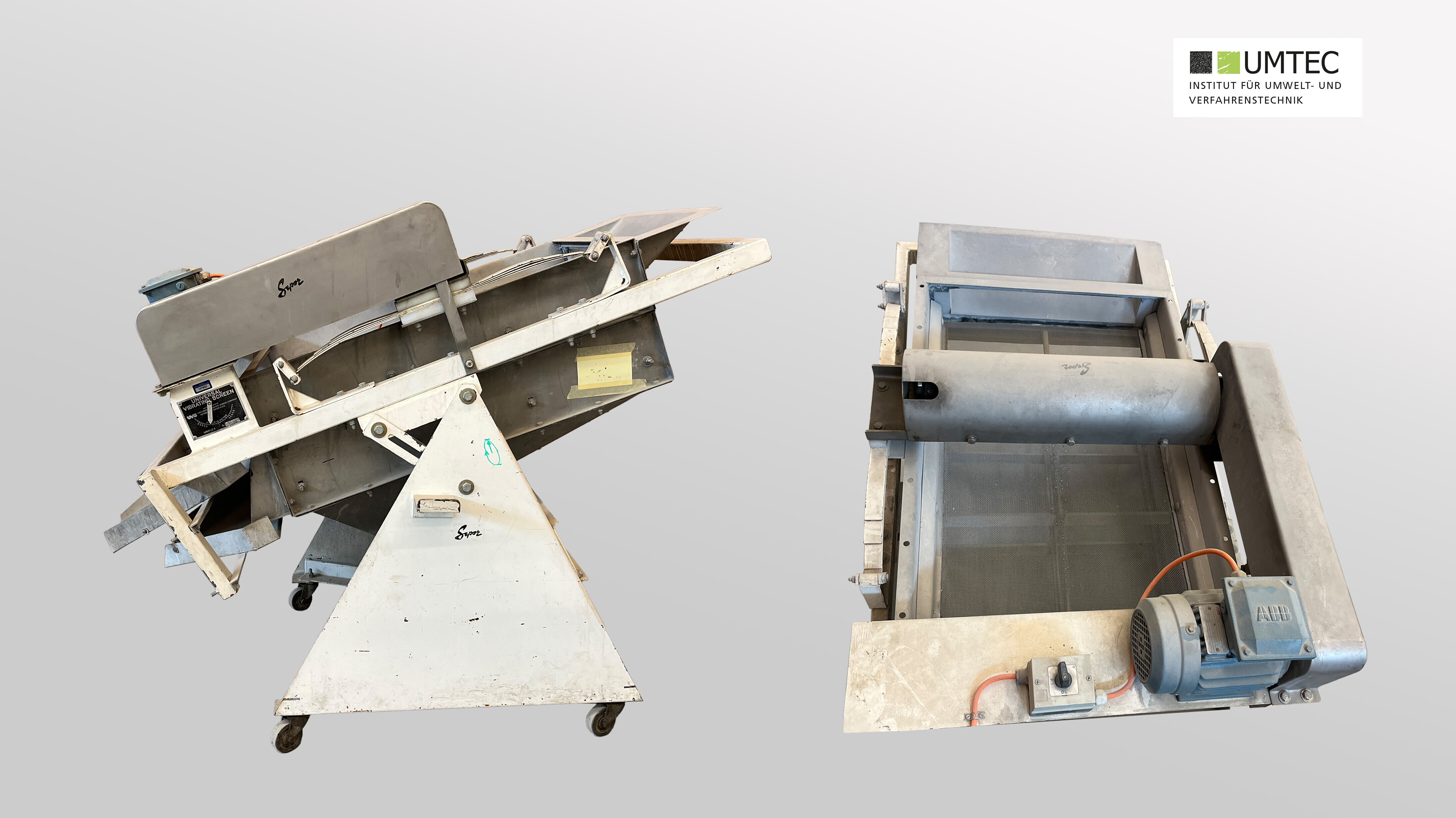
Sieve Towers (Gilson / Laboratory)
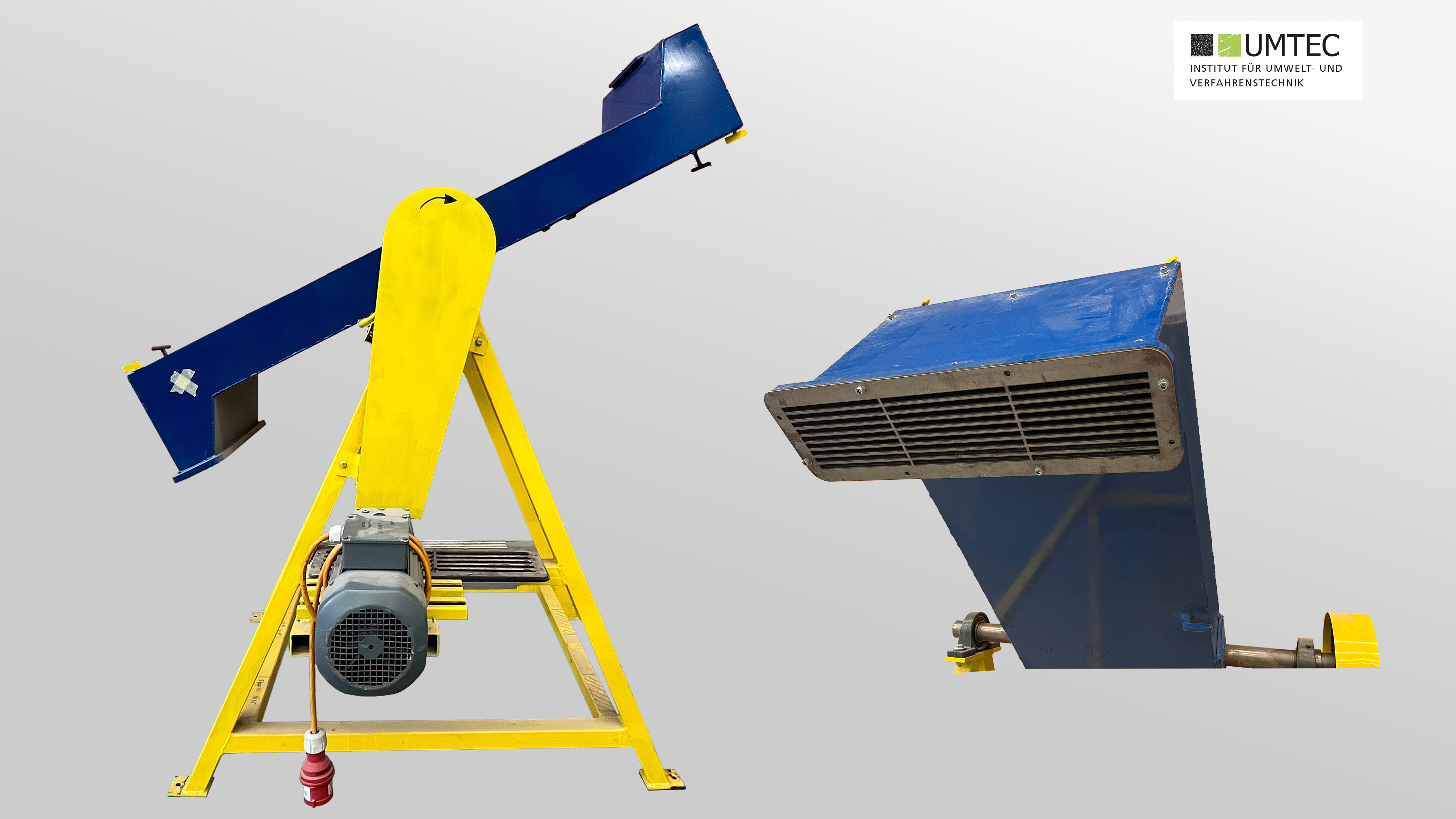
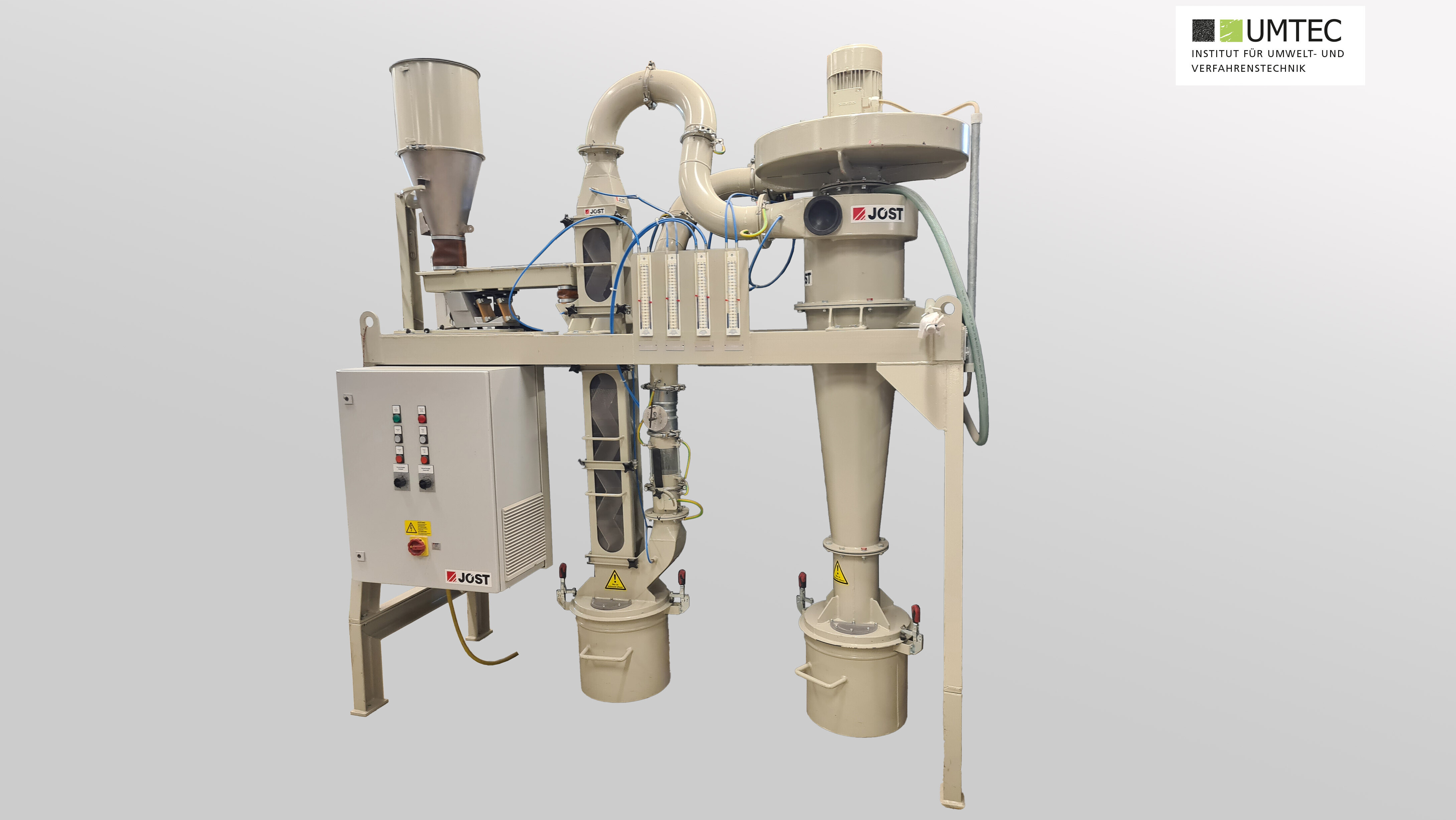
Zigzag Sifter (Jost / Pilot Scale)
Tumbling Sieve Machine (Retsch / Laboratory)
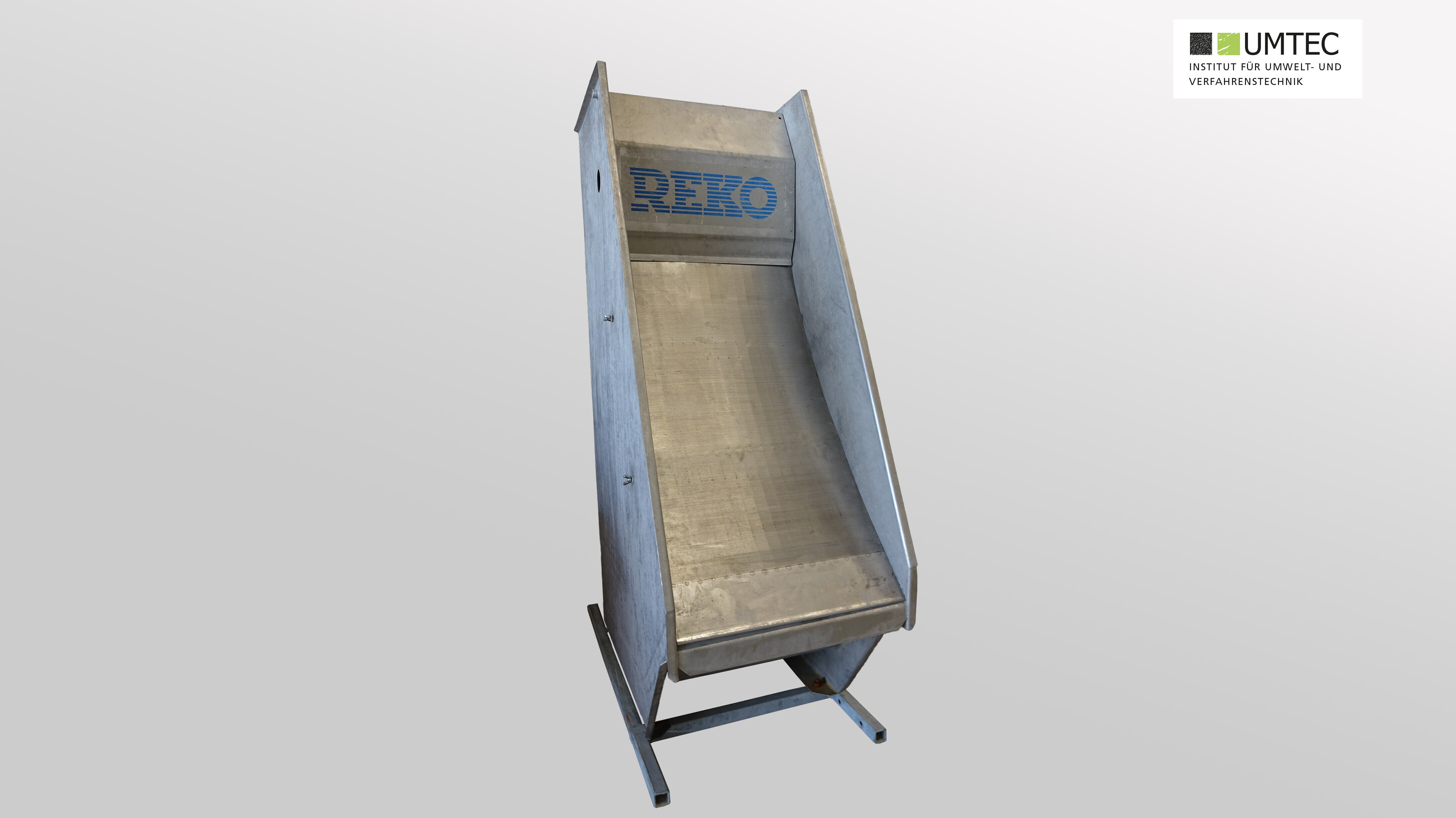
Arc Sieve (Reko / Pilot Scale)
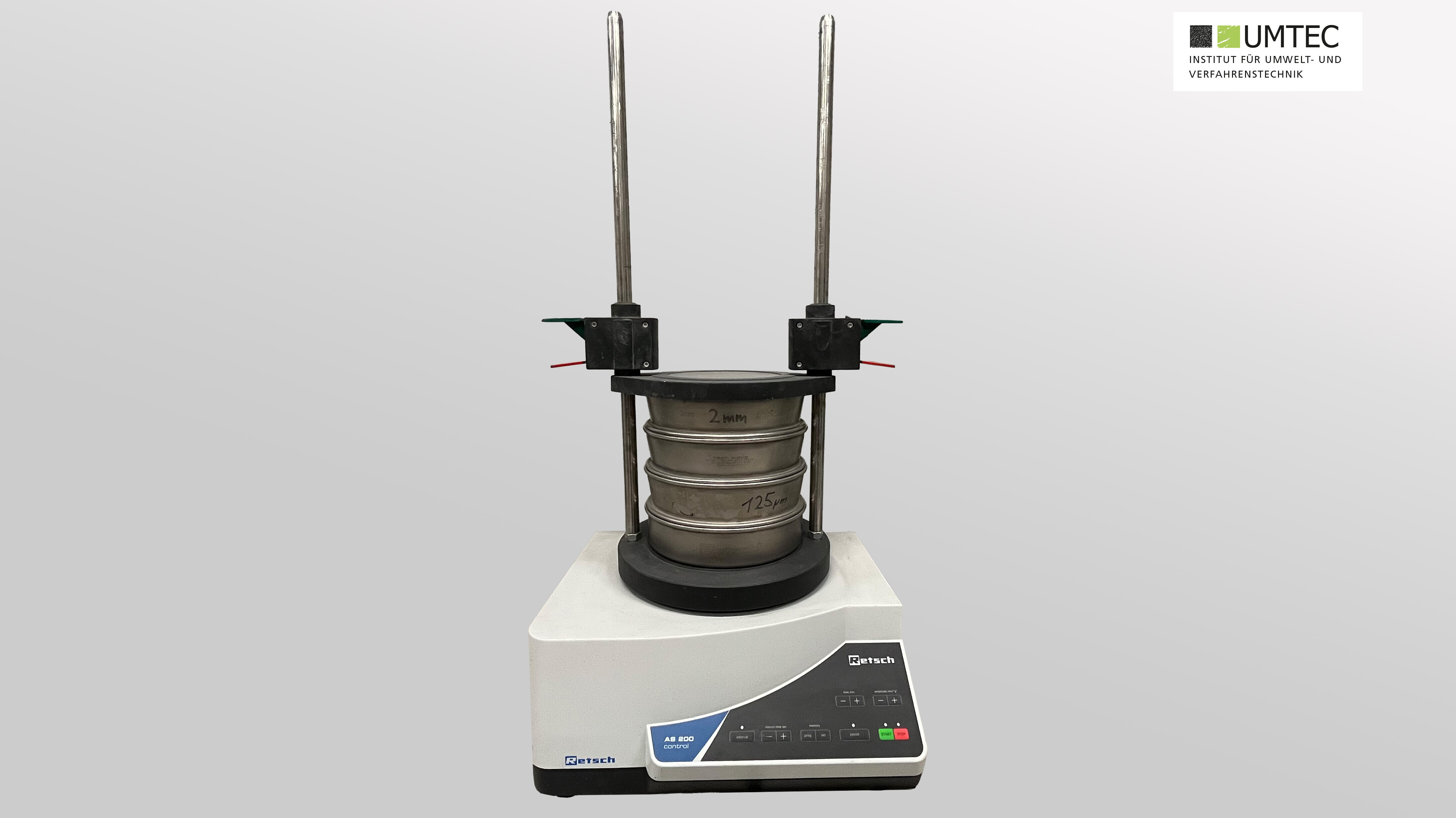
Plan Sieve Tower (Retsch AS 400 control / Laboratory)
Double Deck Sieve (Sepor / Pilot Scale)
- For the continuous screening of material quantities at pilot scale
- Circular vibrating throw sieve
- Arrangement of the eccentric above the center of gravity
- The material is accelerated in the feed area in the direction of transport and decelerated in the discharge area, ensuring optimal utilization of the sieve surface
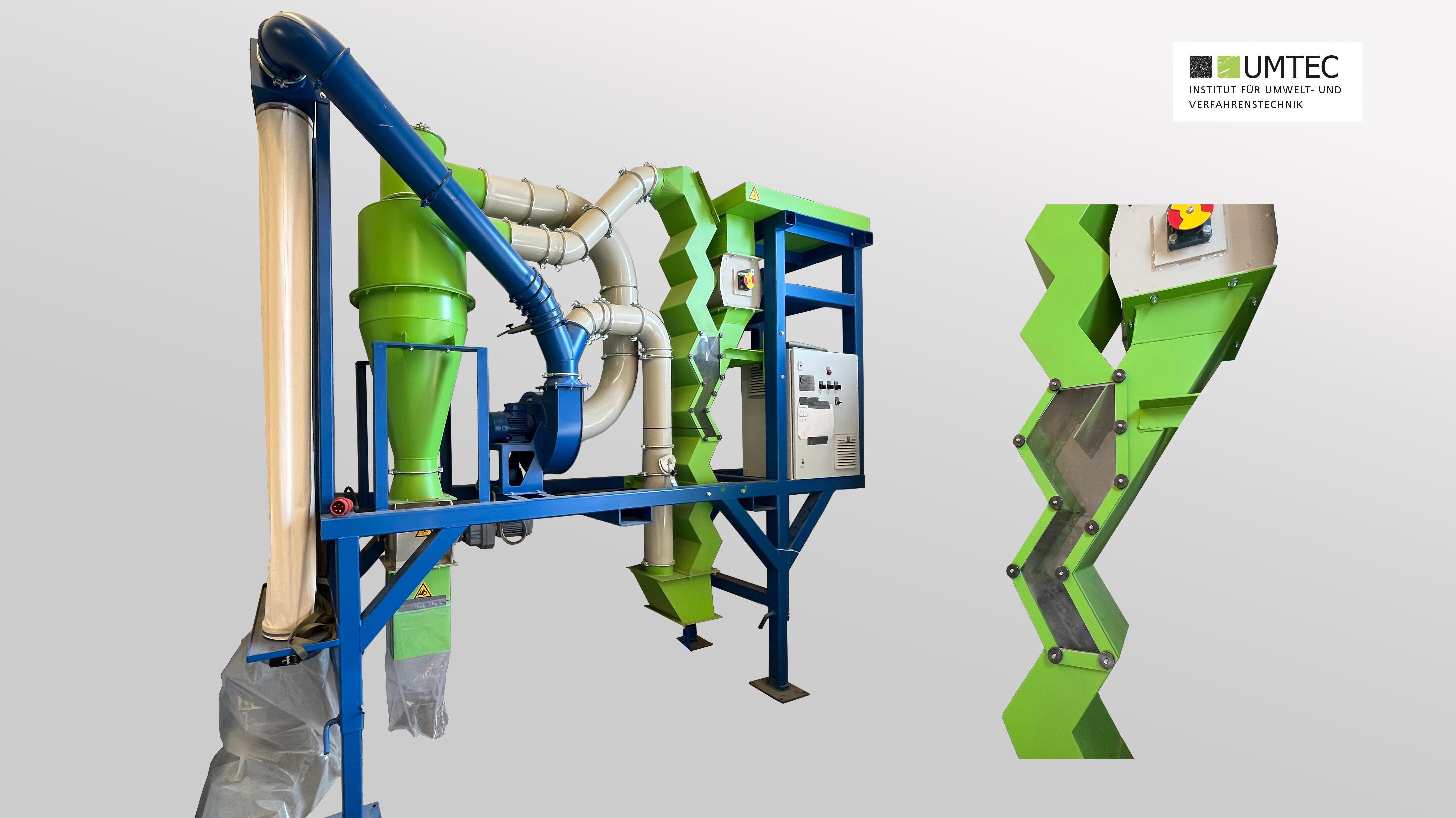
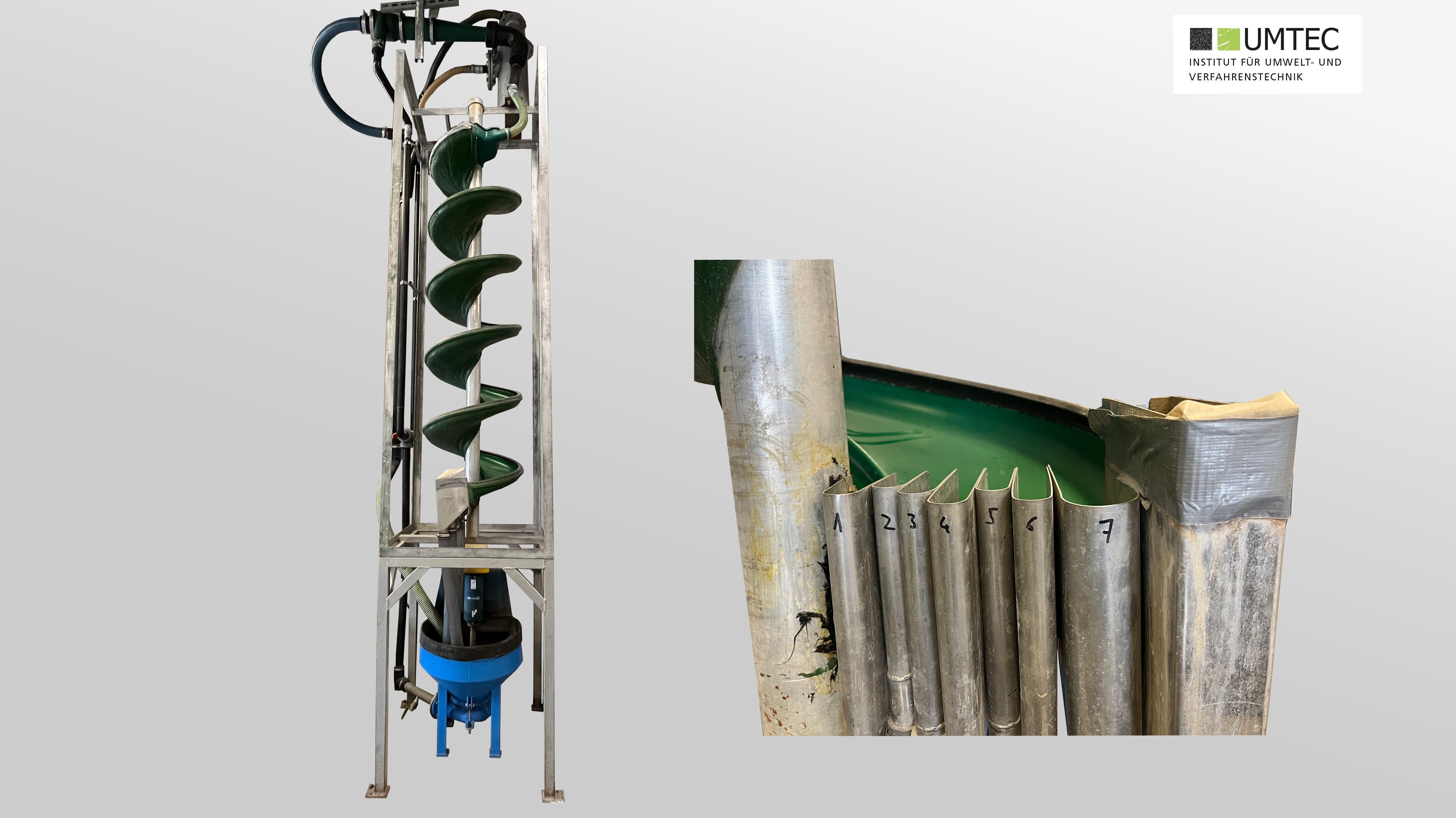
Zigzag Sifter (Recycling World RW ZZS-200-15-SM / Pilot Scale)
- For the continuous separation of material by weight
- Separation occurs based on sedimentation velocity in an upward flowing air stream
- 12 sieving stages with a sifter height of 2200 mm and a sifter width of 180 mm
- Semi-continuous operation with infeed and discharge hoppers (250x250x300 mm)
- Particle size 0.1 mm – 30 mm
- Semi-mobile system on rollers
- Overall dimensions of the system LxWxH 3.5 x 1.06 x 2.98 m
Centrifugal Sifter Bahco (Laboratory)
- The feed material is thrown into a rotating separation chamber. Under the influence of an airflow directed towards the rotational axis and the outward centrifugal force, the material separates according to its sedimentation velocity.
- The separation cut is adjusted by the rotational speed.
- Particle size analysis according to DIN 66120.
Sorting Technology
Sorting is the separation of a granular bulk material into components of different material types or properties. Depending on the device, sorting can be done based on factors such as density, magnetism, or conductivity.
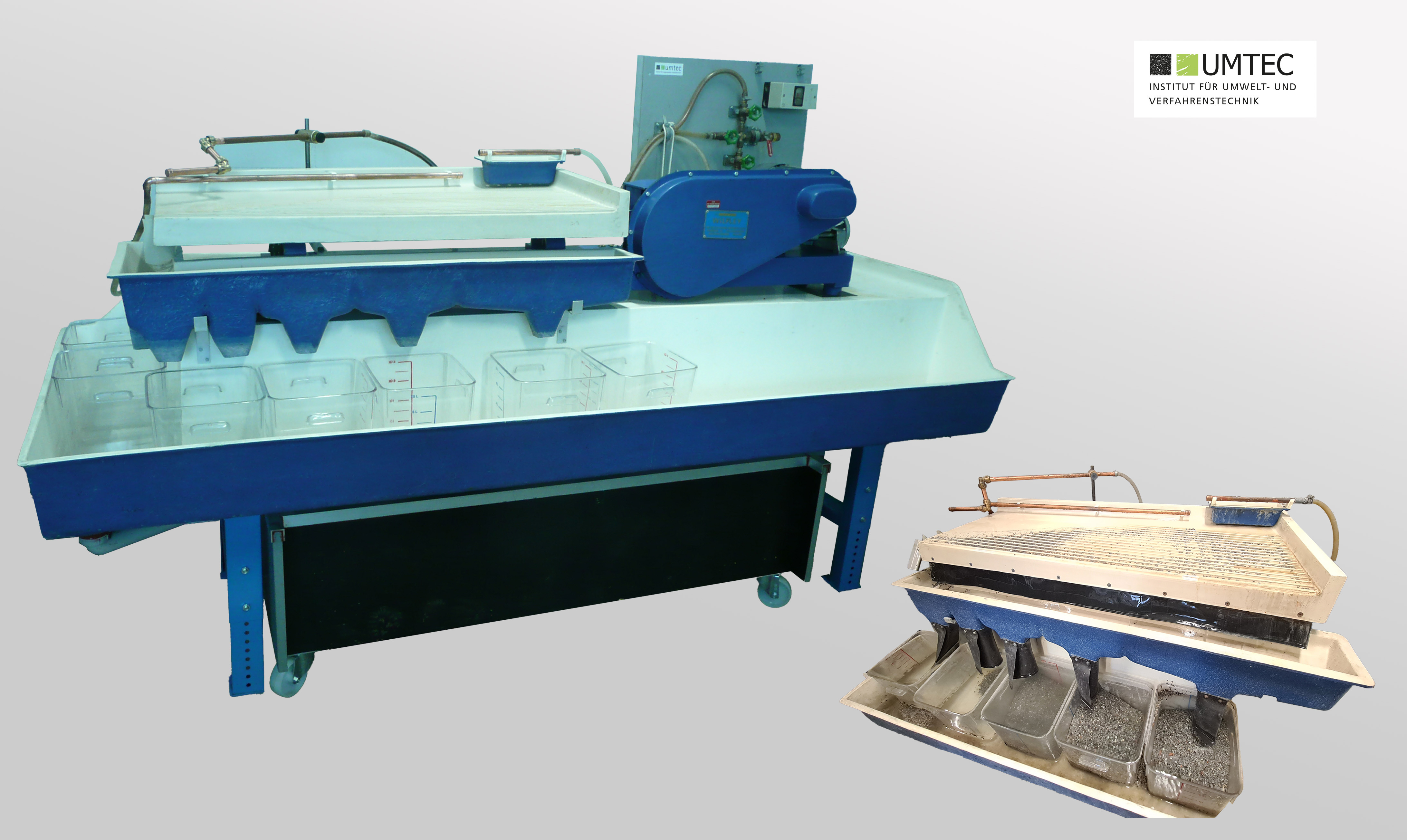
Wet Shaking Table (icscontec / Pilot Scale)
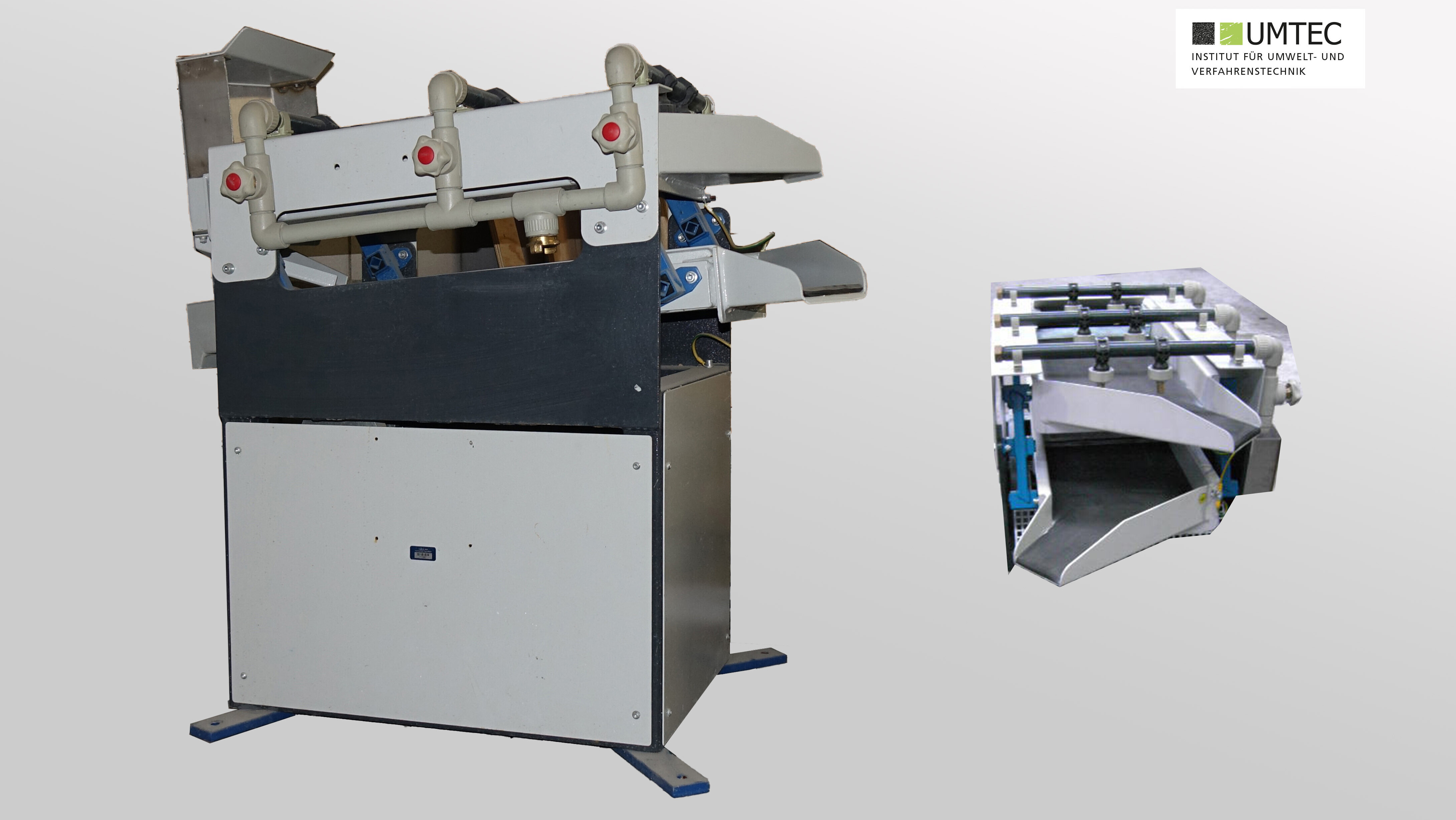
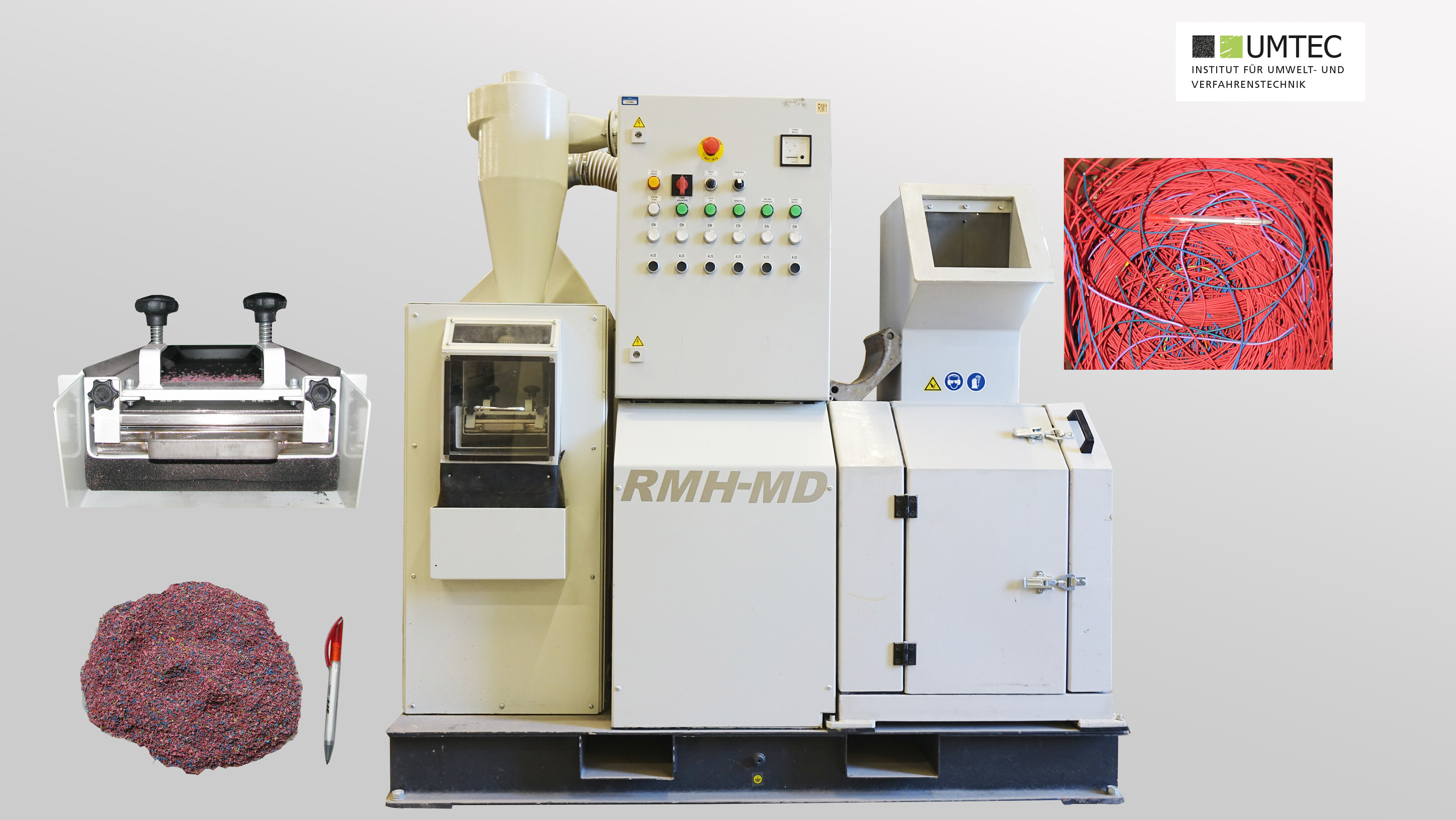
Cable Recycling System (Gertrud Diebels Recycling Machines)
Shaking Table (Wilfley / Pilot Scale)
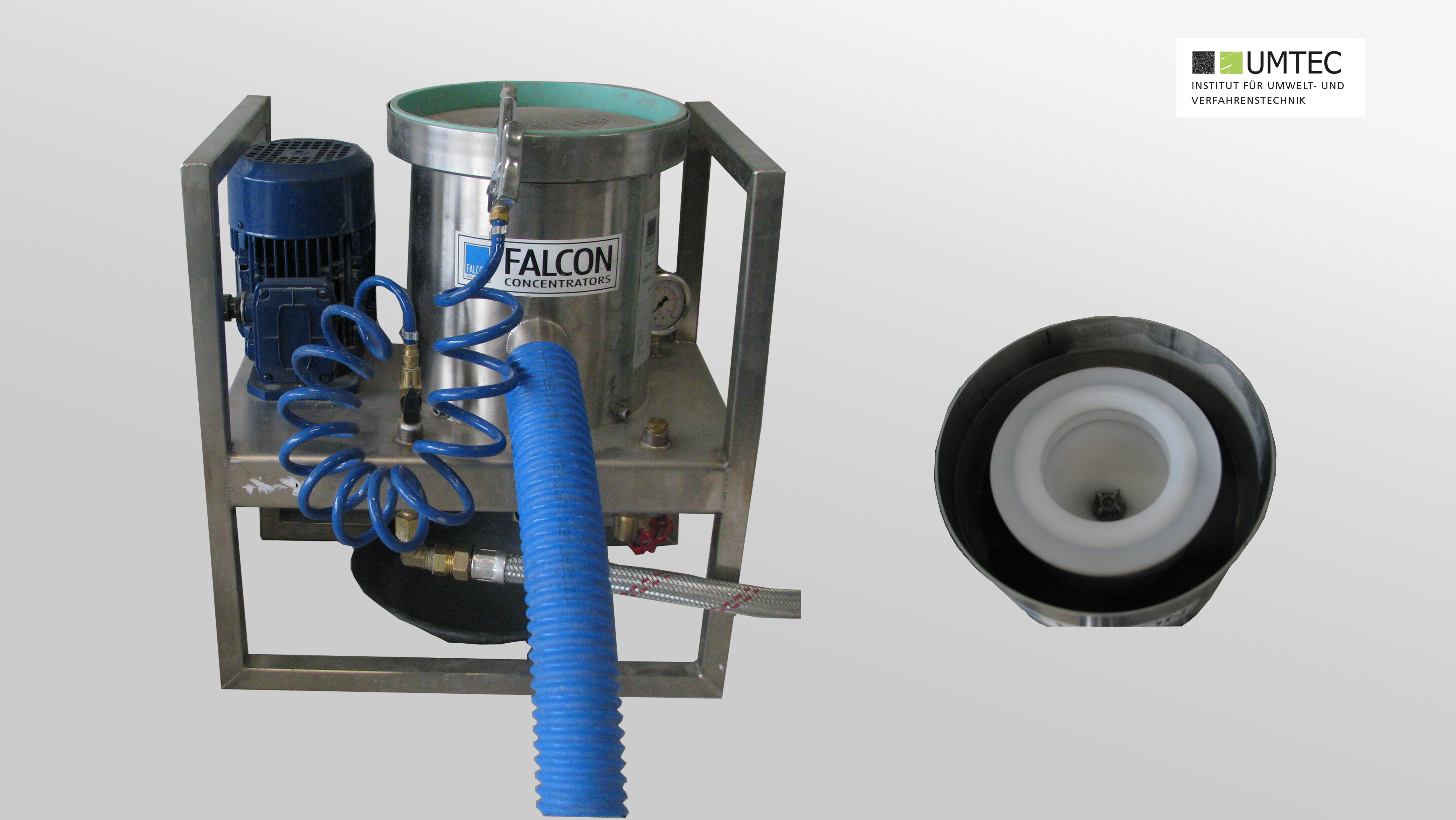
Falcon Concentrator (Sepro / Laboratory)
Air Separation Bed (Triple S Dynamics / Laboratory)
- Separation of fine-grained material based on density
- Fluidization of the material bed through an upward airflow directed through the bed
- Transport of the material through impulsive movements of the table, causing specific light and heavy particles to segregate
- Different density separation cuts are possible by adjusting the vibration frequency/tilt of the table
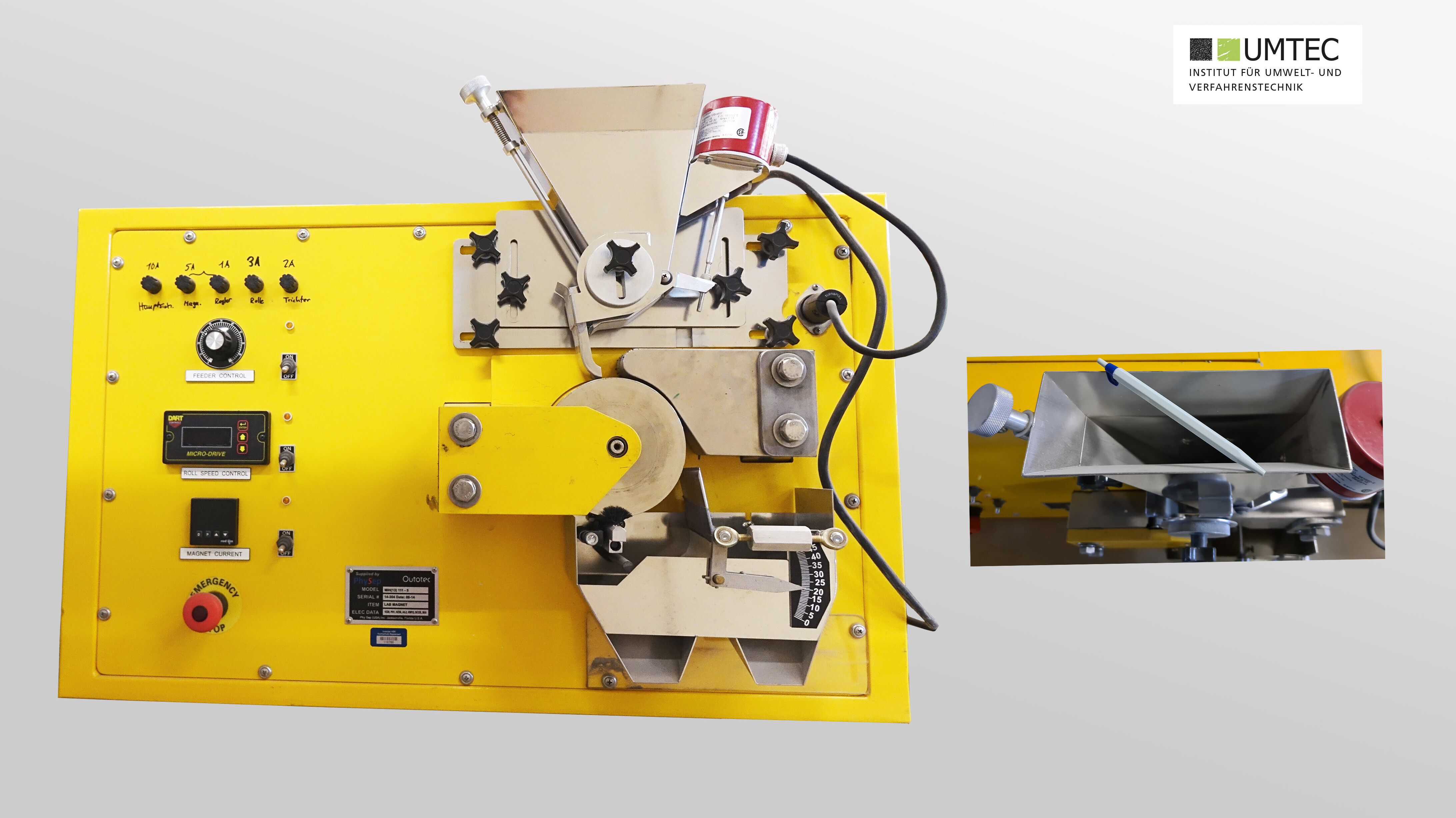
Electrostatic Separator (Outotec / Pilot Scale)
- Separation of conductive particles from non-conductors based on different surface conductivities
- Electrostatic charging of the feed material using high voltage by feeding it onto a rotating and grounded roller
- Conductors discharge their surface charge to the roller and are thrown off
- Non-conductors do not discharge their charge and remain attached to the roller due to electrostatic attraction. They are separated from the roller by a scraper and neutralization electrode after about ¾ of a rotation
- Partially conductive particles (e.g., plastic-metal composites) are removed in a middle fraction
QUERULATOR (In-house Development / Laboratory and Pilot Scale)
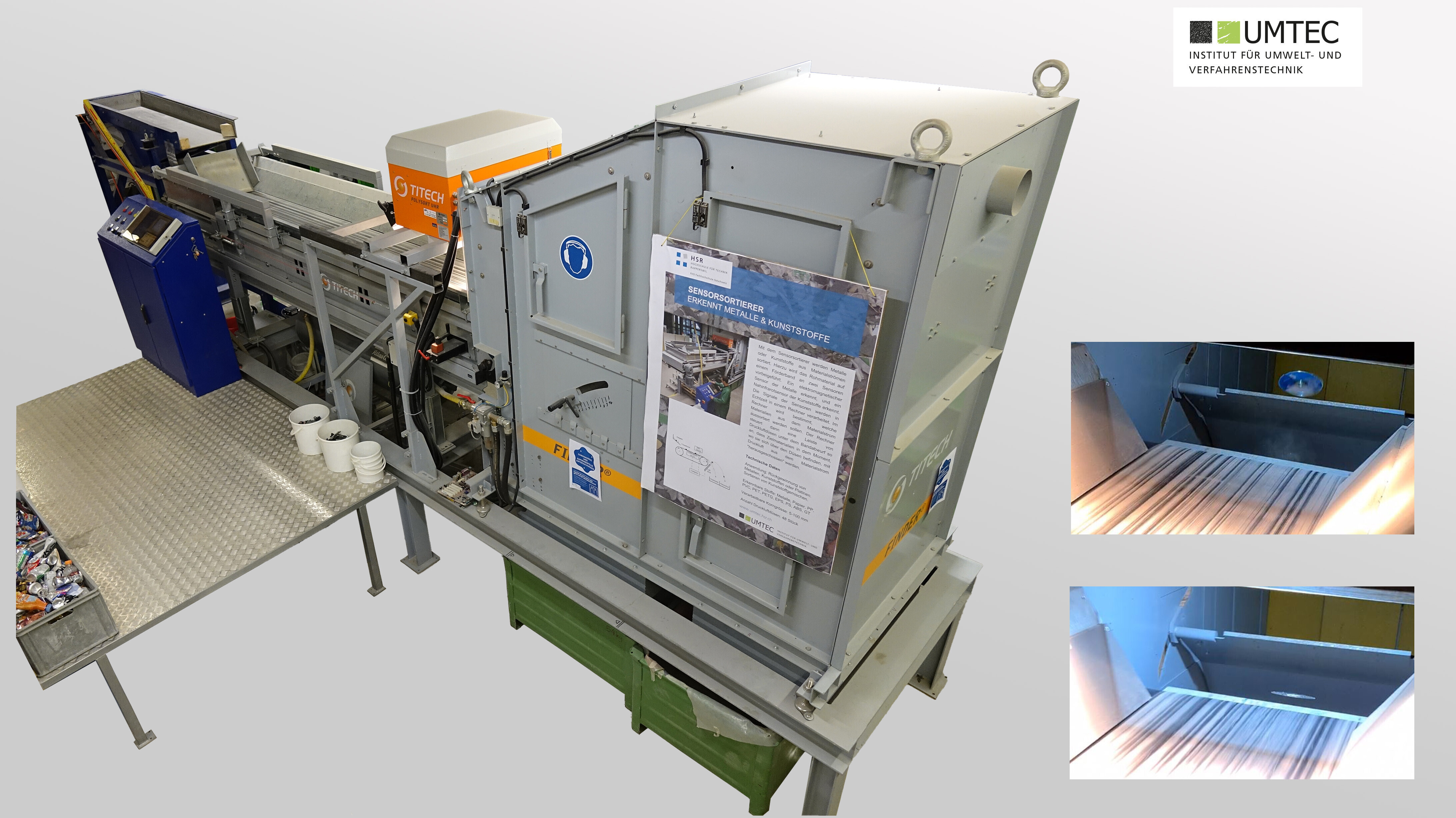
Polysort Finder (Titech / Industrial Plant)
Eccentric Eddy Current Separator (Eriez / Pilot Scale)
- For separating non-magnetic, electrically conductive materials such as aluminum and copper from non-conductors like plastic, glass, slag, etc.
- Permanent magnets on a rapidly rotating pole wheel induce eddy currents in conductive materials. This creates magnetic fields that oppose the induced magnetic fields. Electrically conductive materials are repelled and ejected from the material flow.
- Pole wheel adjustment: 0 – 30 degrees above the top dead center
- Good separation performance for particle sizes <5 mm due to a design optimized for fine grains
High Gradient Magnetic Separator (Outotec / Laboratory)
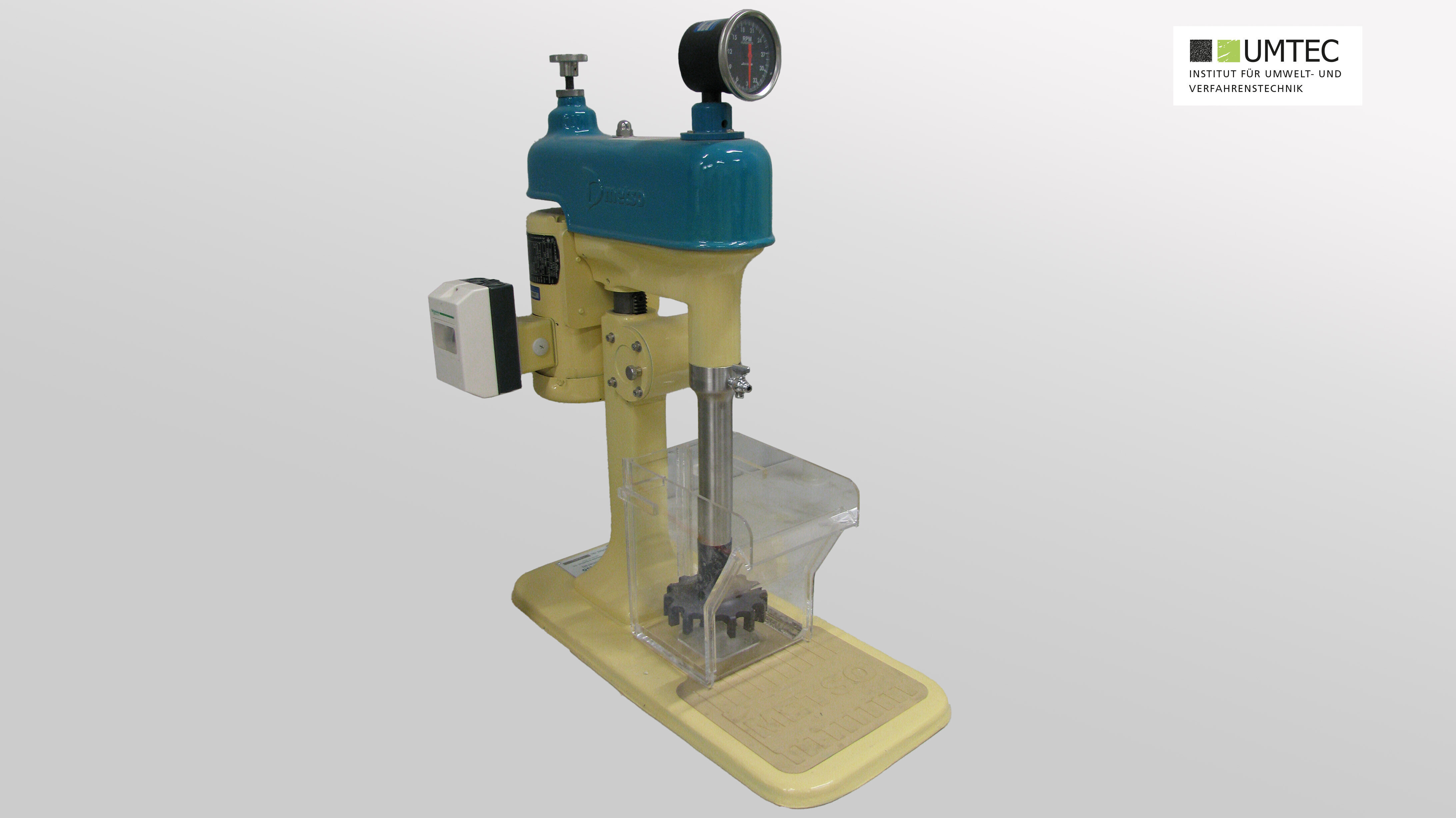
Flotation Cell (Metso Mineral Systems / Laboratory)
- Flotation is a physical/chemical separation process in which a fine-grained solid mixture in aqueous suspension is separated based on the differing surface wettability of the particles. Foam-forming agents are added to the flotation bath, and then air is introduced and finely distributed. The water-repellent particles adhere to the air bubbles, float to the surface, and can be skimmed off with the resulting foam. The non-water-repellent particles sink to the bottom and are removed.
- Dimensions of flotation container: 165x154x250mm
- Working volume: approximately 5.0 liters
Spiral Separator (Multotec / Pilot Scale)
- Separation of particles with different densities through the convection flow in the cross-section of the spiral trough.
- Light particles follow the flow outward,
- while heavy particles move toward the center of the trough due to wall friction and the inward-directed crossflow at the bottom of the trough.
Analysis
Various devices and methods are also available for sample analysis. Particle size distributions, optical or digital magnification of samples, as well as the elemental composition of the sample, are just a few examples of the possible analytical methods.
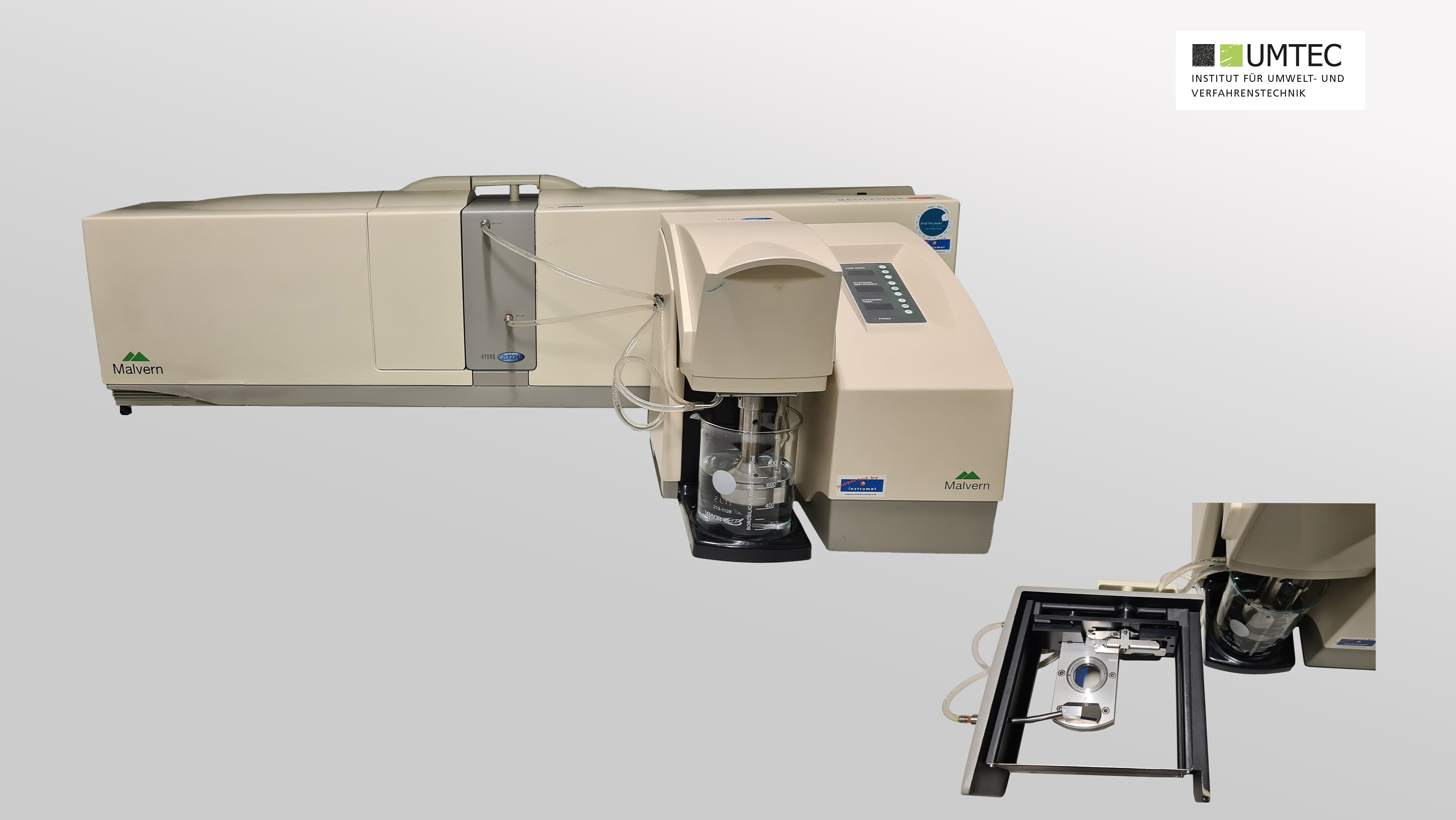
Laser Diffraction Spectrometer (Mastersizer 2000)
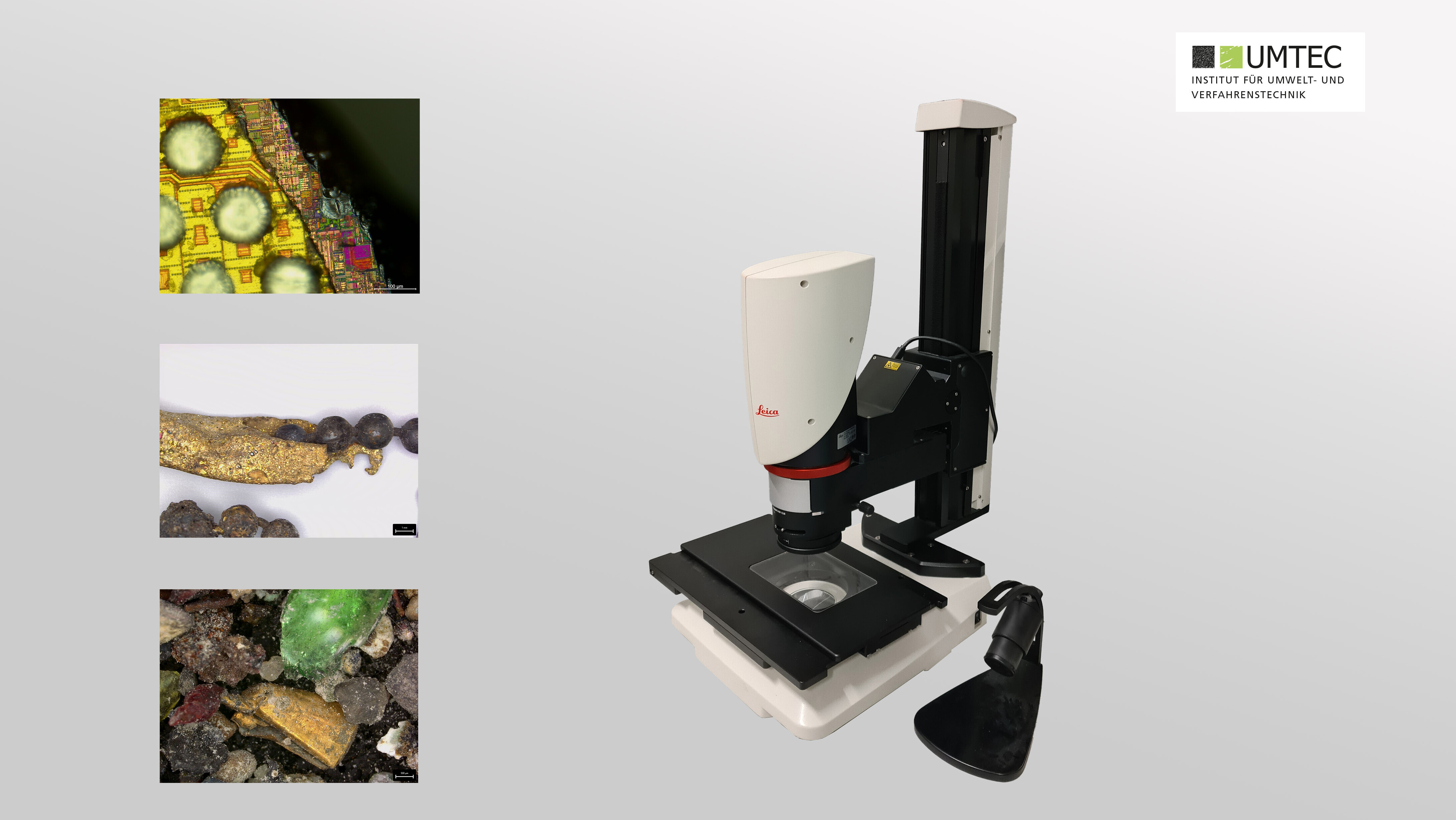
Digital Microscope (Leica DVM 6 M)
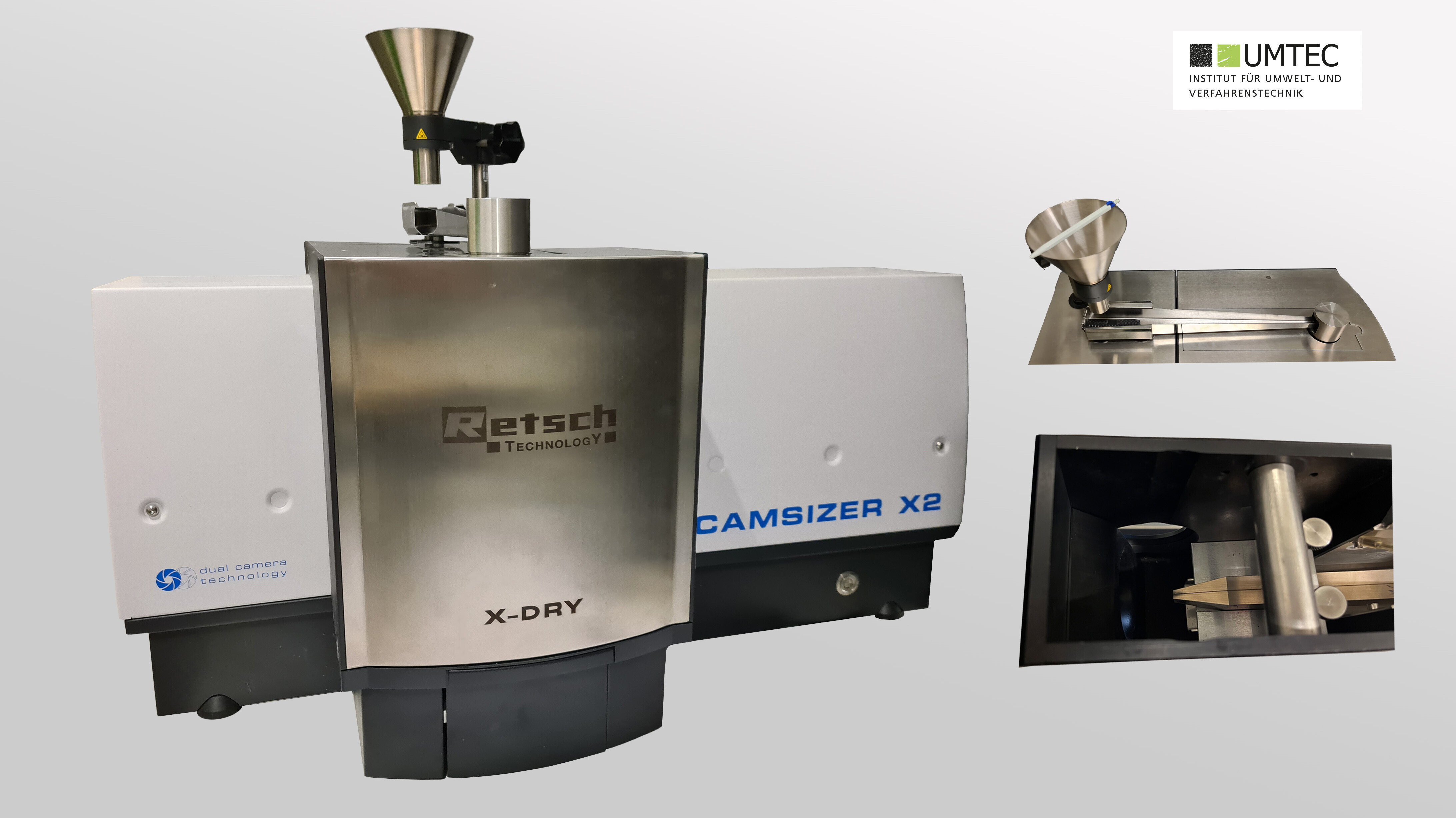
Camsizer X2 (Retsch / Laboratory)
- Measurement of particle size distributions of dry bulk materials
- Measuring range: 0.8 µm – 8 mm
- Utilizes the principle of digital image processing
- The dispersed particle stream passes through two LED strobe light waves, with the shadow projections of the particles being captured by two digital cameras and measured using software.